Navigating the complex world of child-rearing often involves sifting through endless advice and conflicting methodologies. Many parents find success by adopting unconventional approaches that challenge modern societal norms and expectations. These distinctive styles prioritize specific values such as independence or emotional intelligence to shape future generations. Understanding the philosophy behind these methods reveals why they remain popular despite the criticism they often attract.
Free-Range Parenting

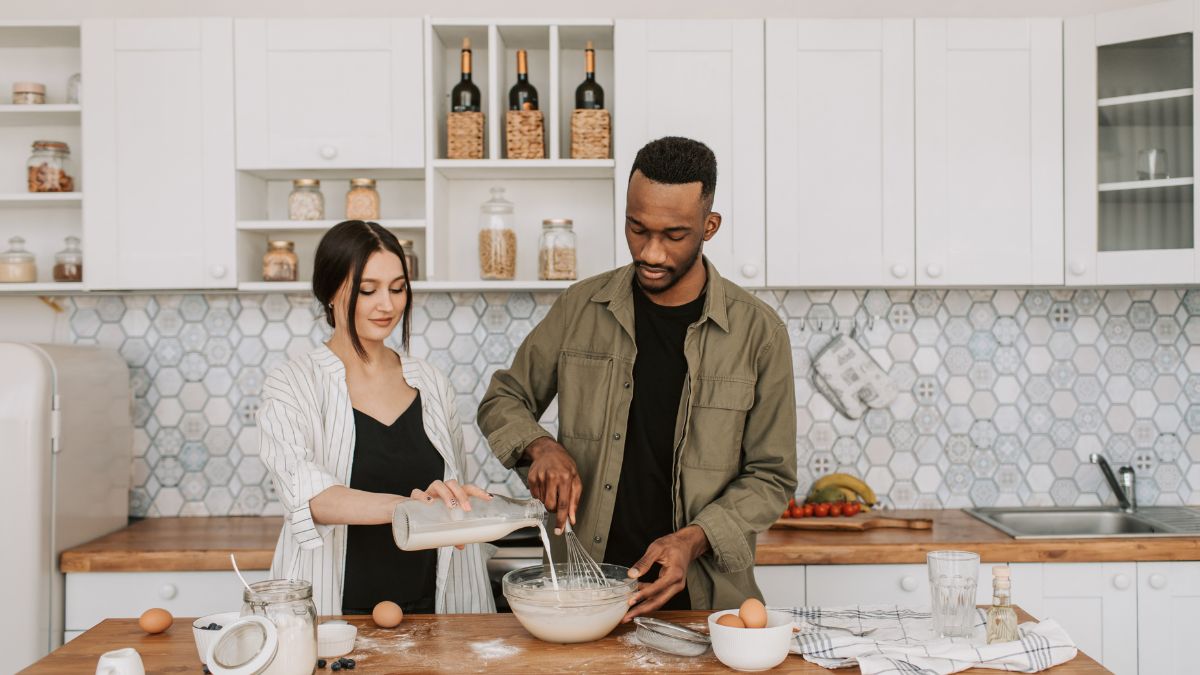
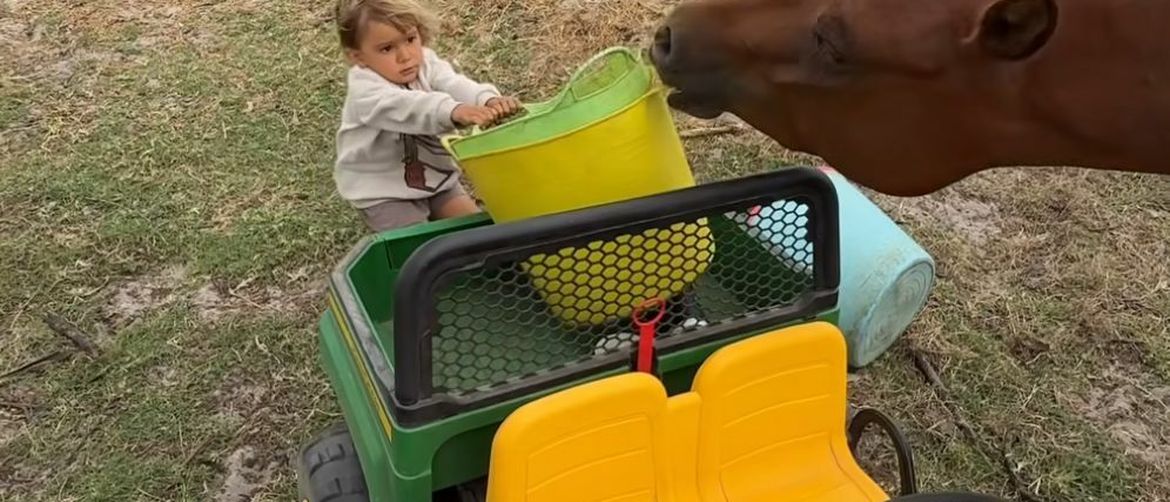
This method encourages children to function independently and without constant adult supervision in public spaces. Parents allow their kids to walk to school alone or play in neighborhood parks at a younger age than current norms usually dictate. The philosophy aims to foster self-reliance and critical thinking skills by letting children navigate real-world challenges on their own. Supporters believe that modern overprotection hinders a child’s ability to assess risk and make safe decisions.
Unschooling

Unschooling rejects standard educational curriculums in favor of learner-chosen activities and real-life experiences. Children pursue their own specific interests such as coding or gardening while parents act as facilitators rather than traditional teachers. Advocates argue that this natural way of learning preserves innate curiosity and creates a lifelong love for knowledge. The method relies heavily on trust in the child and the belief that education happens constantly outside of a classroom setting.
RIE Parenting

Resources for Infant Educarers or RIE treats babies as capable human beings starting from birth. Parents avoid using baby talk and explain every action they take before doing it to the child. This approach emphasizes respect and allowing the infant to develop at their own natural pace without propping them up or forcing milestones. Proponents claim this builds deep trust and confidence between the parent and the child from day one.
Elimination Communication

Parents who practice this method forgo diapers and instead learn to interpret their baby’s signals for needing to relieve themselves. Caregivers hold the infant over a toilet or sink immediately upon recognizing these specific cues. This technique requires intense observation and close physical proximity to the child during the first few months. Enthusiasts argue it reduces waste and prevents diaper rash while strengthening the parent-child bond.
Tiger Parenting

This strict parenting style prioritizes high academic achievement and exceptional performance in extracurricular activities. Parents set demanding standards and often restrict social activities to ensure focus remains on productive pursuits like music or math. The approach is rooted in the belief that rigorous discipline and hard work are the keys to future success and stability. While critics call it harsh, many children raised this way develop strong work ethics and reach elite levels in their fields.
Attachment Parenting

Attachment parenting focuses on forming a secure emotional bond through maximum physical closeness and responsiveness. Practices often include baby-wearing and extended breastfeeding along with co-sleeping arrangements. The goal is to ensure the child feels consistently safe and heard to promote long-term psychological health. Critics worry about parental burnout, but supporters report their children grow up to be more independent and empathetic.
French Parenting
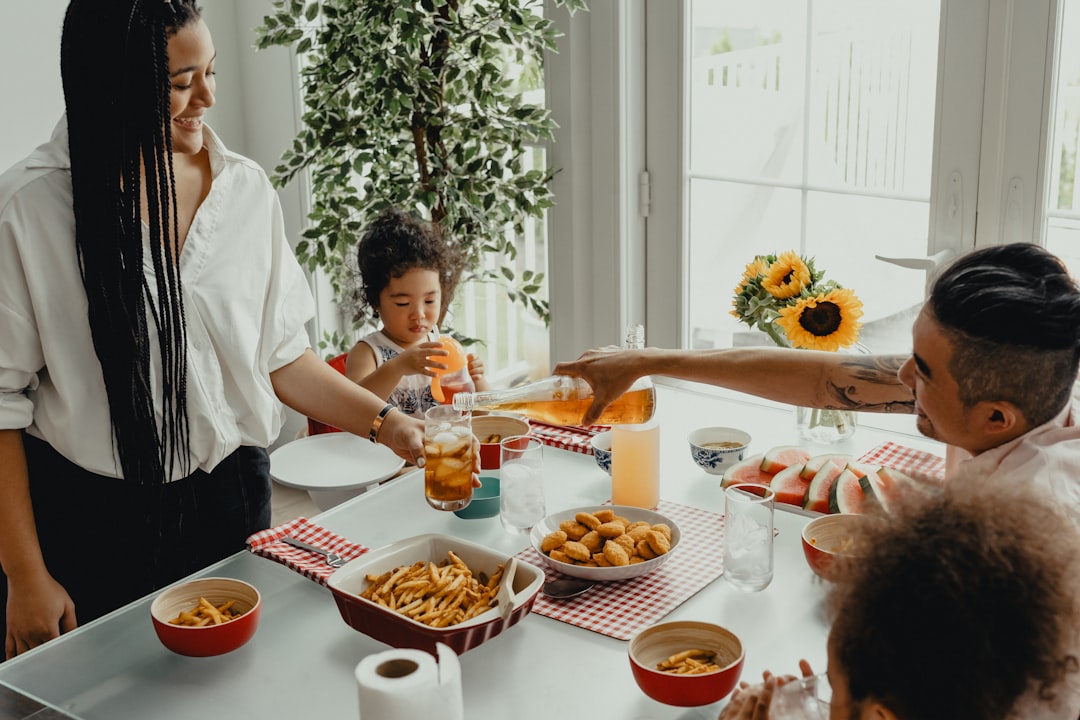

This style emphasizes patience and delayed gratification by not rushing to comfort a child the moment they cry. Parents operate on a strict schedule for meals and sleep to teach children how to adapt to the family rhythm. There is a strong focus on exposing kids to adult foods and expecting them to behave politely in social settings. The result is often a calm household where children understand boundaries and possess advanced social manners.
Baby-Led Weaning
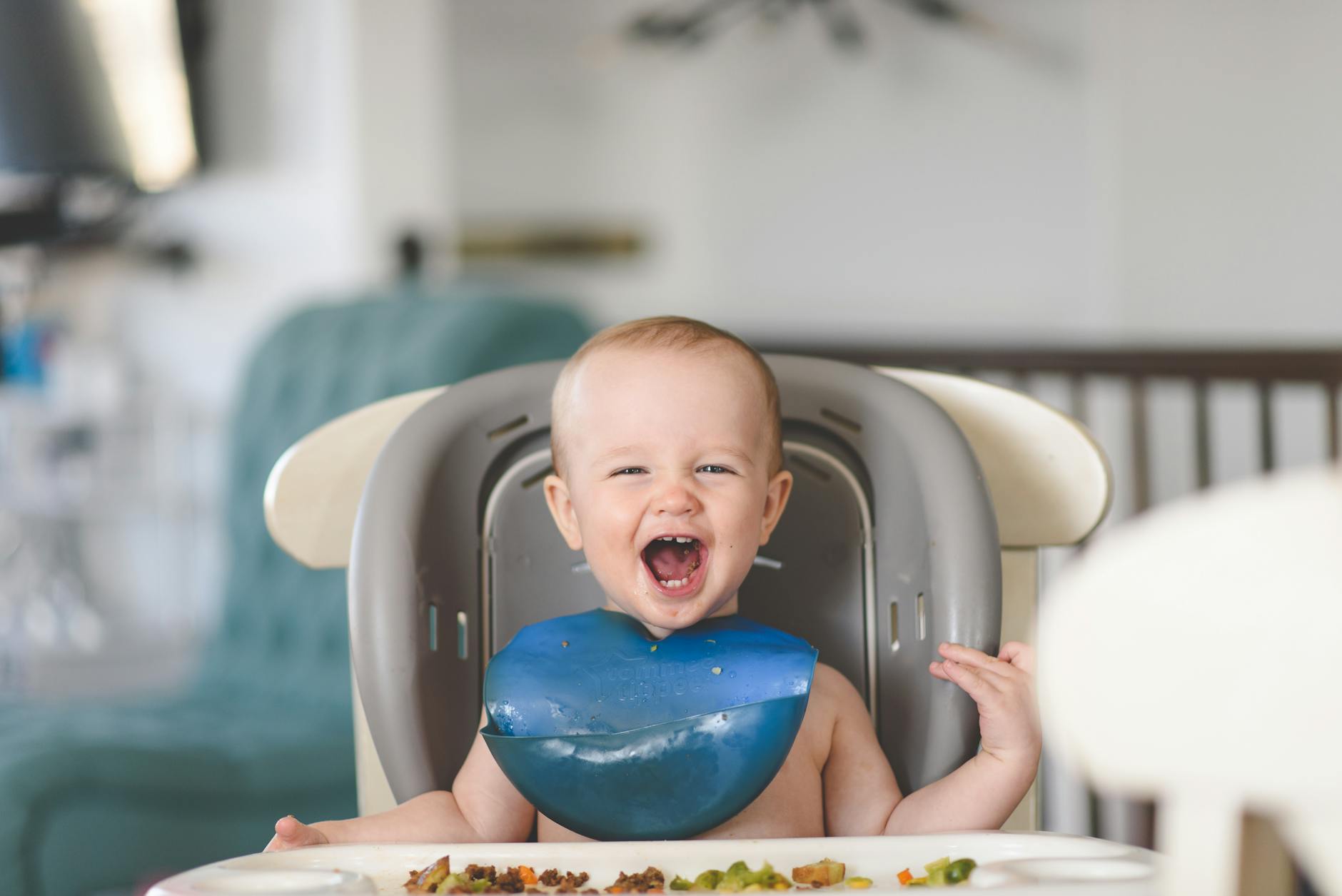

Parents bypass traditional purees and spoon-feeding to offer infants soft finger foods right from the start of solid feeding. The baby sits at the family table and explores textures and tastes at their own pace. This method encourages self-regulation of appetite and helps develop fine motor skills early on. It can be messy and stressful regarding choking hazards, but many find it creates adventurous eaters who enjoy family meals.
Gender-Neutral Parenting

Caregivers intentionally avoid reinforcing traditional gender stereotypes in clothing or toys and language. Children are encouraged to play with trucks or dolls regardless of their biological sex. The objective is to allow the child to develop their own identity without the constraints of societal expectations. This approach aims to prevent the limitations that gender roles can place on a child’s potential interests and career paths.
Slow Parenting
This philosophy pushes back against the trend of over-scheduling children with endless lessons and organized sports. Parents prioritize unstructured play and downtime to allow creativity and relaxation to flourish. The focus is on quality time and reducing the stress that comes with a hurried lifestyle. Advocates believe that boredom is actually beneficial because it forces children to invent their own entertainment and discover their passions.
Radical Honesty

Parents using this style tell their children the truth about everything regardless of the topic or complexity. They avoid myths about fictional characters and answer difficult questions about life and death with factual accuracy. The intention is to build a relationship based on absolute trust and to treat children as rational beings. While some argue it robs kids of childhood magic, others say it prepares them better for the real world.
Yes Parenting

Caregivers strive to say yes to their children’s requests as often as possible unless there is a direct safety risk. The environment is arranged so that fewer restrictions are necessary and exploration is encouraged. This method reduces power struggles and helps children feel their desires are valid and heard. Supporters claim it fosters a cooperative relationship where children are more likely to listen when a rare no is spoken.
Extended Co-Sleeping

Families share a bed or sleep in the same room well beyond the infant years and sometimes into late childhood. This practice is common in many cultures and promotes a sense of security and communal rest. Parents believe it simplifies nighttime parenting and reduces anxiety for the child. While controversial in Western medicine due to safety concerns, many families report better sleep quality for everyone involved.
World Schooling

This educational approach uses travel as the primary means of teaching children about history and culture. Families often sell their possessions to live as nomads while the world becomes the classroom. Children learn languages and geography through immersion rather than textbooks. It requires immense privilege or lifestyle alteration, but it produces globally minded citizens with unique adaptability skills.
Simplicity Parenting

Parents drastically reduce the number of toys and books and activities available to their children. The home environment is kept clutter-free to prevent overstimulation and promote deep focus. Daily rhythms and rituals are established to provide a predictable and soothing atmosphere. Proponents argue that having less stuff allows children to value what they have and engage more deeply in imaginative play.
Introduction of Allergens Early

Contrary to older medical advice, many parents now introduce high-risk foods like peanuts and eggs to infants as early as four months. This proactive approach aims to train the immune system to tolerate these substances before an allergy develops. It requires careful monitoring and consultation with pediatricians to ensure safety. Recent studies suggest this method significantly lowers the rates of severe food allergies in the population.
Academic Acceleration

Parents advocate for their children to skip grades or enter college at a very young age to match their intellectual capabilities. The focus is on providing appropriate mental stimulation rather than keeping the child with their age peers. This style prioritizes cognitive development and prevents the boredom that can lead to behavioral issues in gifted students. Critics worry about social development, but many accelerated students thrive in environments that challenge them.
Dolphin Parenting

This balanced style combines a firm set of rules with a nurturing and flexible attitude. Parents act as collaborative guides who encourage independence while maintaining a safety net. The approach values emotional intelligence and creativity alongside responsibility. It is often seen as a happy medium between the strict Tiger and the permissive Jellyfish styles of parenting.
Consultant Parenting

Caregivers act as advisors who offer choices and consequences rather than dictators who issue orders. They let children make mistakes and face the natural outcomes of those decisions to learn responsibility. The goal is to transfer the burden of decision-making to the child as they grow. This method prepares children for adulthood by teaching them how to solve problems without constant rescue.
Commando Parenting

This rigid style involves strict adherence to routine and immediate compliance with commands. Parents run the household with military precision to ensure efficiency and discipline. Expectations for behavior and contributions to the family are set very high. While it lacks warmth in the traditional sense, it produces children who are highly organized and respectful of authority.
Intuitive Eating for Kids

Parents avoid restricting sugar or labeling foods as good or bad to prevent disordered eating habits. Children are trusted to listen to their own hunger and fullness cues to regulate their intake. The house is stocked with a variety of foods including treats to neutralize their appeal. Supporters believe this prevents obsession with forbidden foods and fosters a healthy relationship with eating.
Risky Play

This approach allows children to engage in activities that involve speed or heights and dangerous tools. Parents stand back while kids climb tall trees or use real hammers to build things. The philosophy is that children need to encounter risk to learn how to manage it safely. Proponents argue that removing all danger creates anxious children who are prone to accidents.
Cry It Out

This sleep training method involves letting a baby cry for specified periods to teach them to soothe themselves. Parents check on the child at intervals but do not pick them up or feed them. The goal is to establish uninterrupted sleep patterns for the entire family. While emotionally difficult for parents, it is effective at establishing independent sleep habits quickly.
Gentle Parenting

Gentle parenting focuses on empathy and understanding the root cause of a child’s behavior. Parents use positive language and connection rather than punishment or timeouts to guide actions. The method requires immense patience and emotional regulation from the adult. Advocates claim it builds a brain wired for emotional intelligence and self-control.
Digital Minimalism

Families strictly limit screen time and delay the introduction of smartphones until late adolescence. The home emphasizes physical books and board games over video games and social media. Parents model this behavior by keeping their own devices out of sight during family time. The aim is to protect children from the negative effects of technology on attention spans and mental health.
Bilingual Immersion

Parents speak exclusively in a non-native language to the child or enroll them in immersion schools from a young age. This requires a significant commitment to maintaining the second language in the home environment. The cognitive benefits include improved problem-solving skills and executive function. It can be challenging if the parent is not fluent, but the long-term cultural and brain benefits are substantial.
Farm Raising
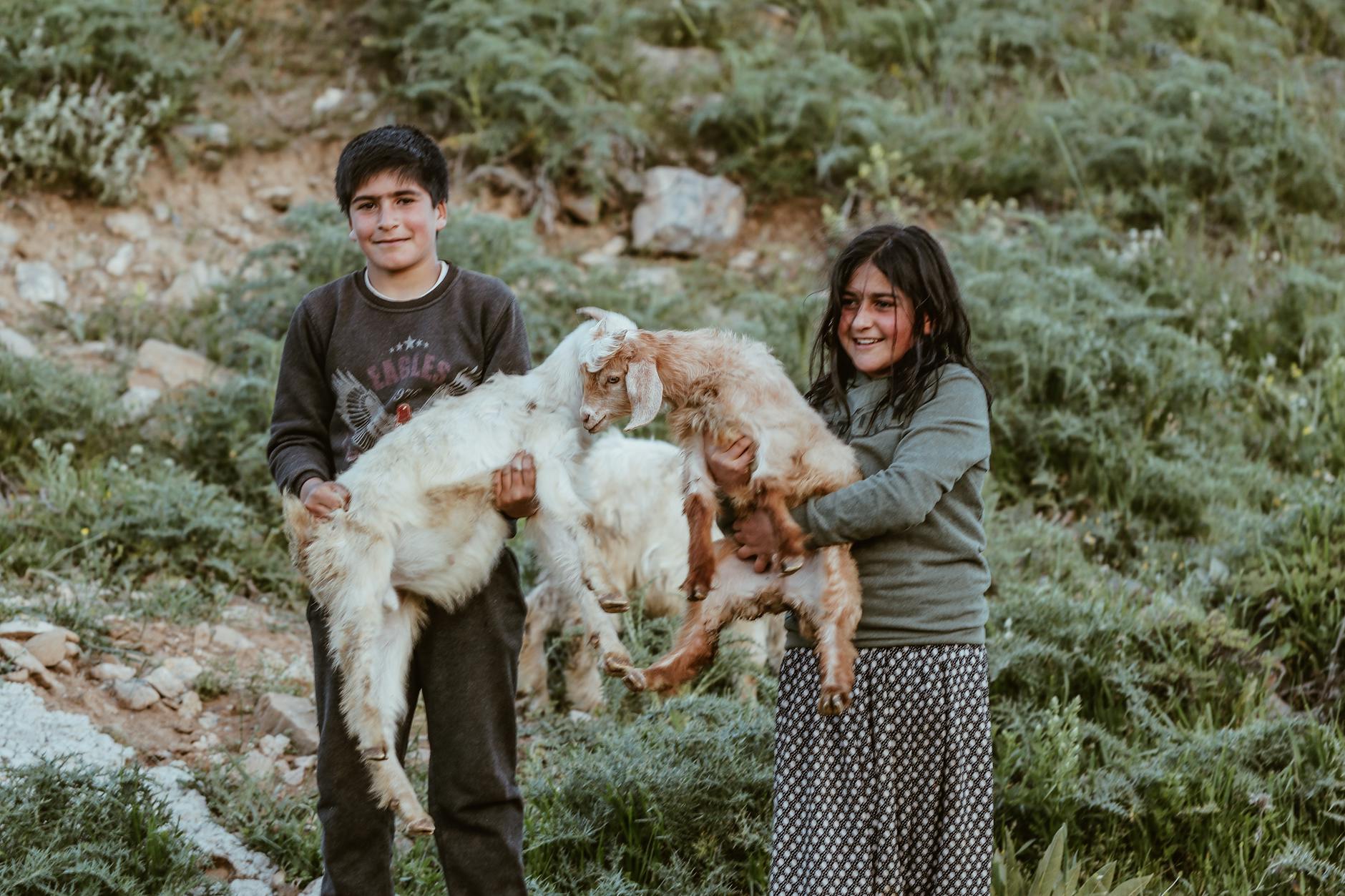

Children are raised in rural environments where they are responsible for caring for animals and crops. The lifestyle demands early mornings and hard physical labor regardless of the weather. Kids learn the cycle of life and the value of hard work through direct experience. This connection to nature and food sources fosters a grounded perspective and robust physical health.
Assigning Heavy Chores
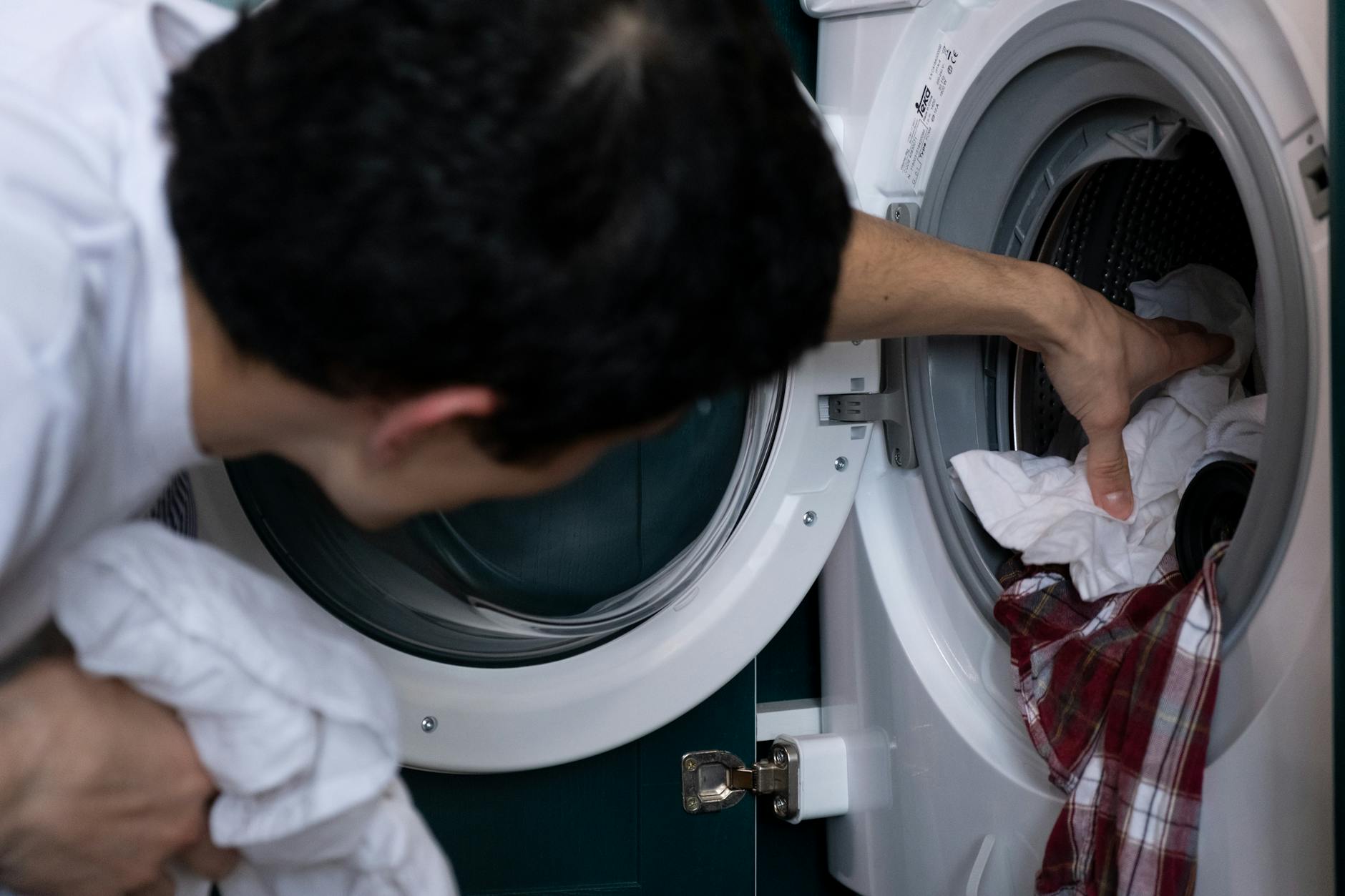

Parents require children to perform significant household tasks such as cooking dinner or doing their own laundry. These are not paid chores but expected contributions to the family unit. The belief is that children feel more capable and needed when they have real responsibilities. This prepares them for independent living better than those who have everything done for them.
Financial Transparency

Parents openly discuss the family budget and salaries and bills with their children. Kids sit in on financial discussions to understand the cost of living and the consequences of spending. This honesty removes the taboo around money and teaches financial literacy through real-world examples. The result is often a young adult who is savvy about saving and debt avoidance.
Allowing Swearing

Some households permit children to use curse words provided they are not used to insult others. Parents treat these words as just another part of language rather than forbidden fruit. The rule usually focuses on context and understanding when such language is inappropriate socially. Supporters find that removing the stigma takes away the power of the words and leads to less usage overall.
No Homework Rule

Parents actively opt their children out of take-home school assignments to preserve family time. They communicate with teachers to ensure learning happens within school hours only. The priority is placed on rest and extracurricular interests over academic drills at home. This controversial stance aims to prevent burnout and keep the love of learning alive.
Lighthouse Parenting
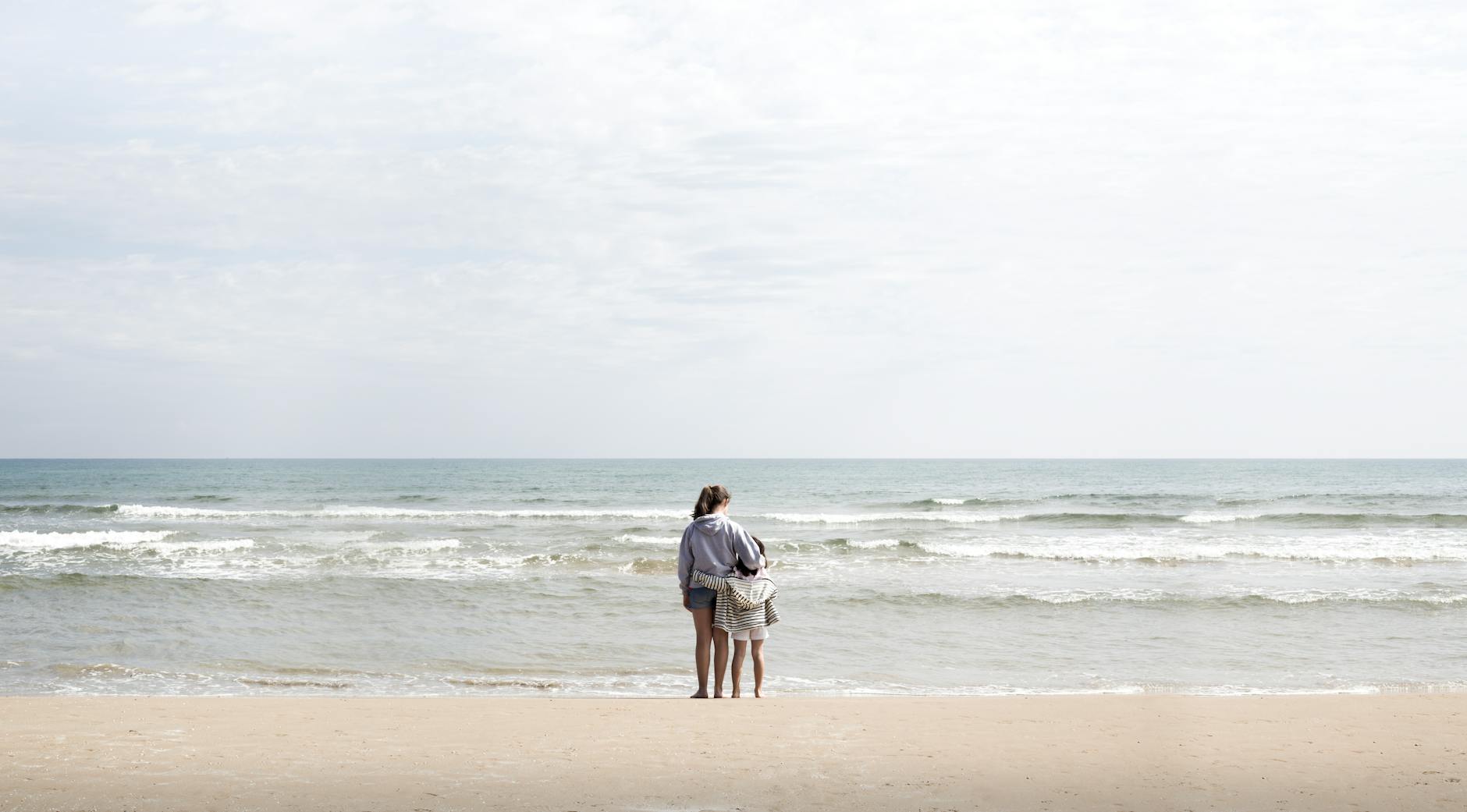

This style involves parents who make themselves visible and available but do not hover over the child. They act as a stationary beacon of safety that the child can return to after exploring the waves of life. The parent trusts the child to handle small struggles but intervenes during major storms. It strikes a balance that allows for growth while ensuring the child never feels truly abandoned.
Please share your thoughts on these parenting styles in the comments.





