Maintaining optimal health requires a delicate balance of nutrients that power every bodily function from cellular repair to energy production. The body frequently sends subtle signals when it lacks essential vitamins or minerals needed for peak performance. These physical cues often manifest as minor annoyances or cosmetic changes long before they develop into serious medical concerns. Recognizing these early indicators allows individuals to adjust their diets and restore equilibrium through targeted nutrition. Understanding these signs is the first step toward reclaiming vitality and supporting long-term wellness.
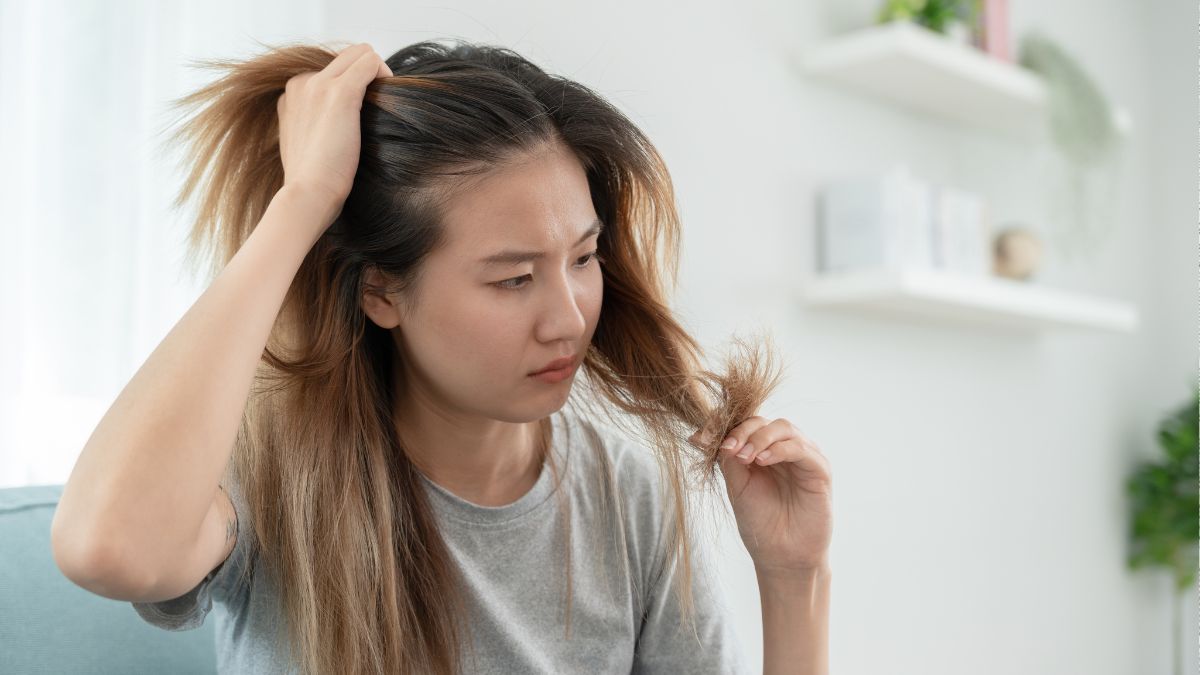
Brittle Hair And Nails

Thinning hair or splitting nails often signals a lack of biotin which is also known as vitamin B7. The body needs this nutrient to convert food into energy and maintain healthy protein structures. Long periods of antibiotic use or anti-seizure medications can sometimes lead to this depletion. Many people address this issue by consuming more egg yolks and nuts or taking specific supplements. Continued fragility suggests a consultation with a healthcare professional might be necessary.
Mouth Ulcers
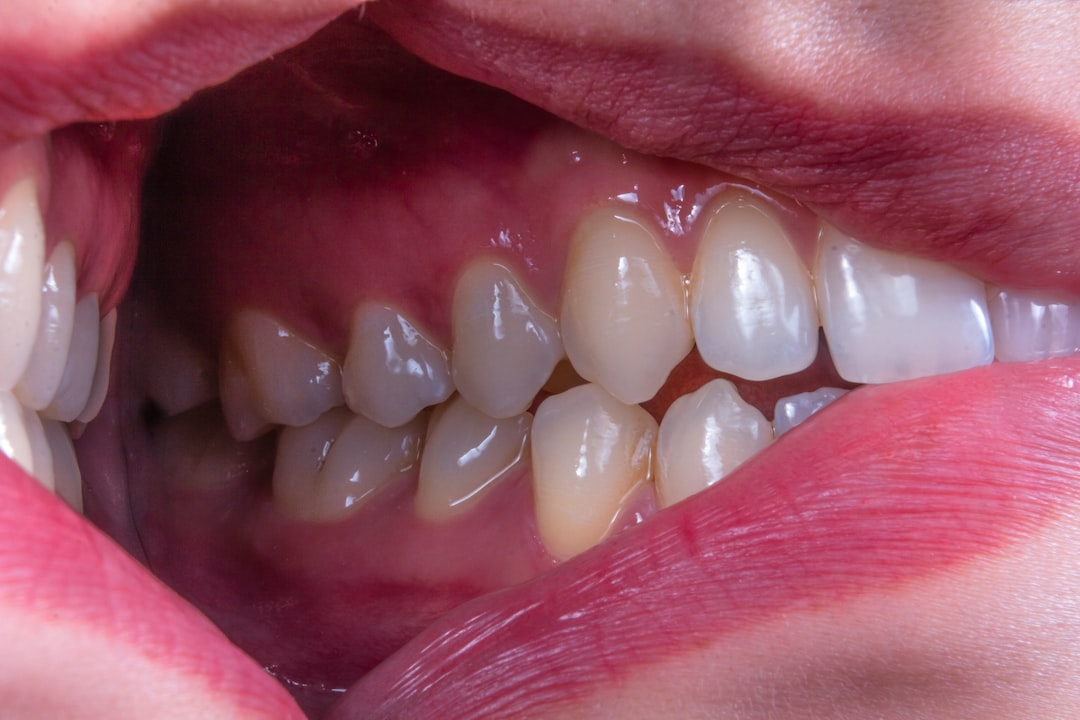
Recurrent sores inside the mouth often indicate insufficient iron or B vitamin intake. These small and painful lesions typically appear on the soft tissues of the cheeks or lips. Studies suggest that low levels of thiamine and riboflavin contribute significantly to their frequent recurrence. Eating red meat and poultry or dark leafy greens helps replenish these necessary stores. A balanced diet usually clears up these mouth sores within a few weeks.
Bleeding Gums
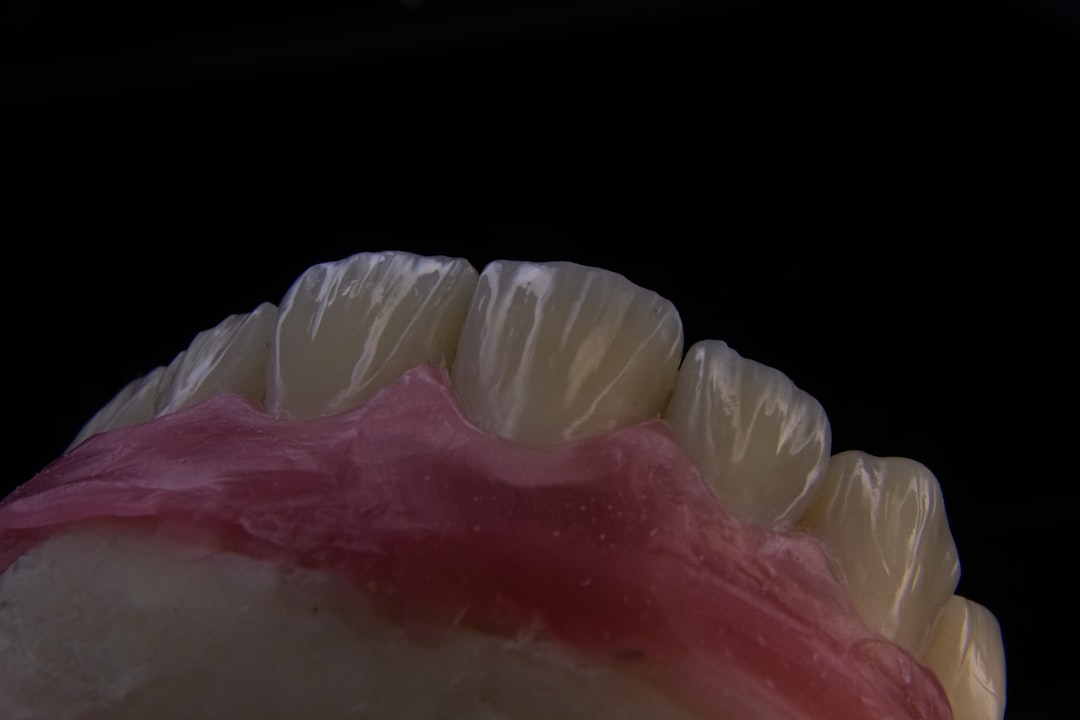
Rough brushing is not always the culprit when gums start to bleed during oral hygiene routines. A diet lacking in adequate vitamin C prevents the body from repairing gum tissue effectively. This essential nutrient acts as a powerful antioxidant and plays a vital role in wound healing. Severe deficiencies can lead to scurvy which causes teeth to loosen over time. Adding citrus fruits and bell peppers to daily meals usually resolves this problem quickly.
Poor Night Vision

Difficulty seeing in low light often points to a lack of vitamin A in the diet. This condition creates a struggle for the eyes to adjust when moving from bright to dark environments. The nutrient is essential for the production of rhodopsin which is a pigment found in the retina. Untreated deficiencies can eventually lead to more permanent damage or dryness of the cornea. Consuming orange vegetables like carrots or sweet potatoes provides beta carotene to support ocular health.
Scaly Skin Patches
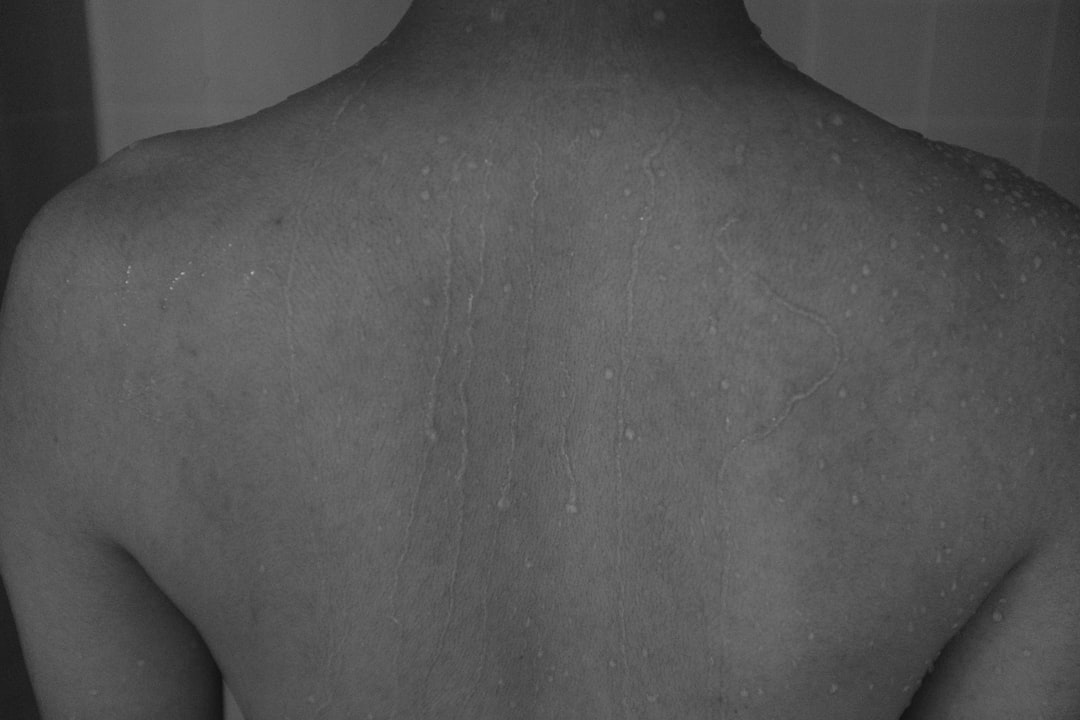
Seborrheic dermatitis creates itchy and flaky patches on the skin that resemble dandruff. This condition frequently stems from low levels of zinc or niacin in the bloodstream. The skin requires these minerals to regulate oil production and maintain a protective barrier. Deficiencies usually result from a diet low in whole grains and quality proteins. Topical treatments may help but dietary changes provide the most lasting relief.
Unexplained Hair Loss
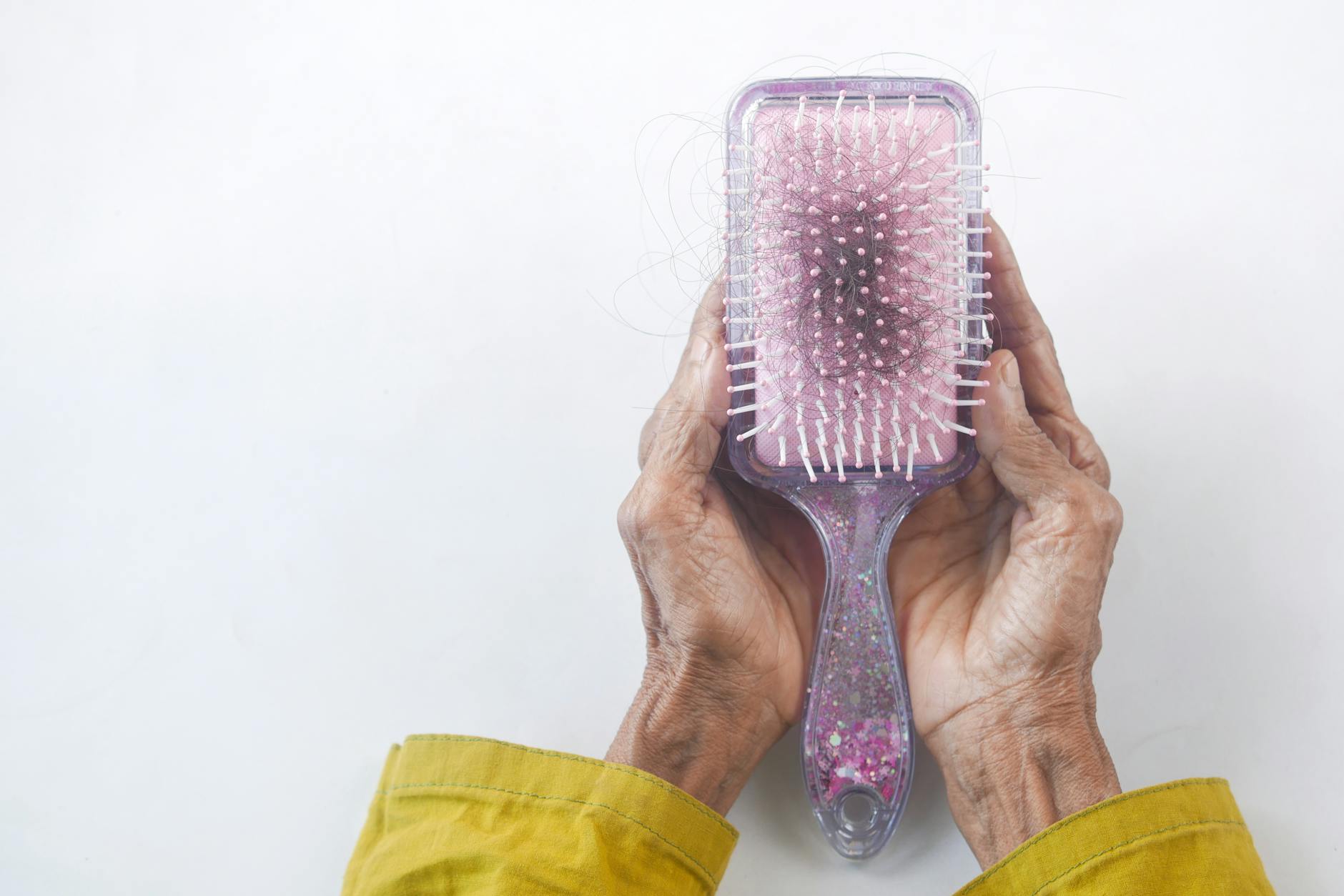

Sudden or excessive hair shedding often points to low iron levels or zinc inadequacy. Hair follicles require these minerals to sustain the growth phase of the hair cycle. A lack of these nutrients forces hair into the resting phase causing it to fall out prematurely. Vegetarians often struggle with this due to the lower absorption rate of non-heme iron. Increasing intake of legumes and pumpkin seeds supports stronger and fuller hair growth.
Red Or White Bumps On Skin
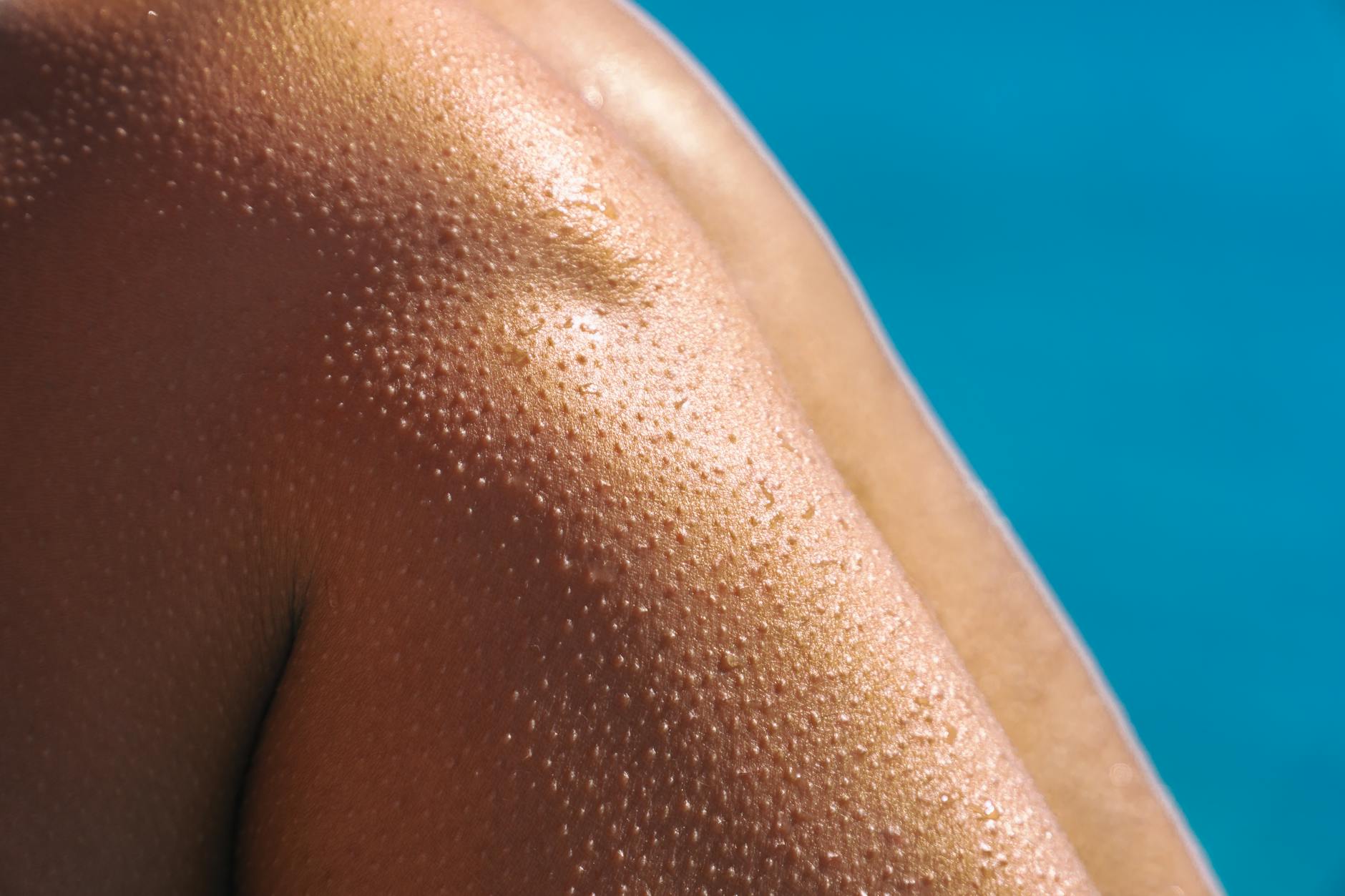
Keratosis pilaris appears as small bumps on the backs of arms or thighs. These bumps indicate the body may need more vitamin A and vitamin C to break down keratin properly. The excess keratin plugs hair follicles and creates a rough texture similar to sandpaper. This condition is genetic but often worsens when nutritional intake drops below optimal levels. A diet rich in colorful fruits and healthy fats helps smooth the skin over time.
Restless Leg Syndrome
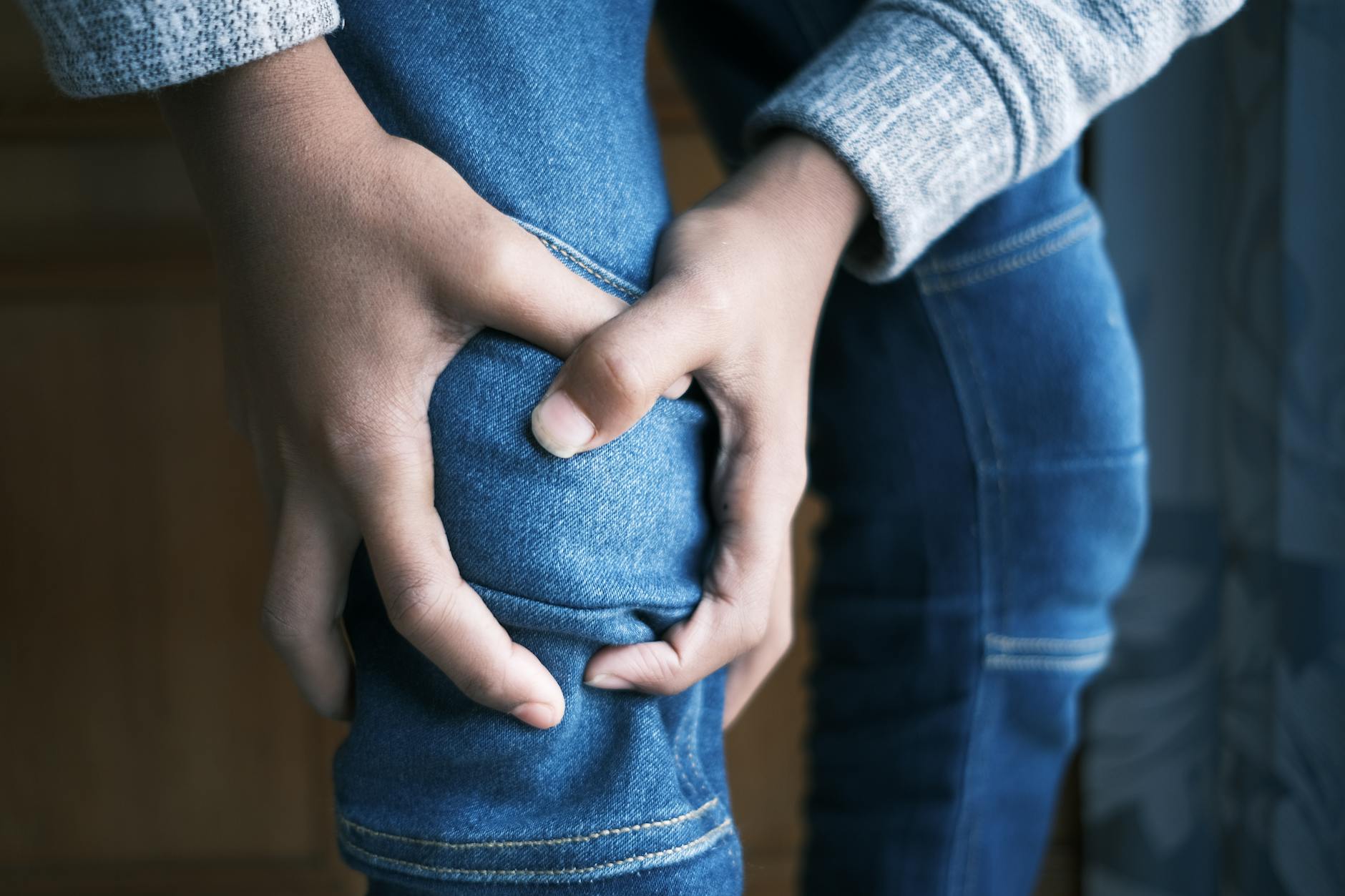

An uncontrollable urge to move the legs while resting is a primary symptom of iron deficiency. The sensation typically worsens at night and disrupts sleep patterns significantly. This condition links directly to how dopamine functions in the brain with the help of iron. Low ferritin levels in the blood are the most common diagnostic finding for this issue. Supplementation under medical supervision often alleviates the discomfort within a few months.
Muscle Cramps

Frequent sharp pains in the calves or toes often suggest a lack of magnesium or potassium. These electrolytes play a crucial role in muscle contraction and relaxation signals. Heavy sweating during exercise depletes these minerals rapidly and requires immediate replenishment. Eating bananas and avocados or almonds provides a quick source of these essential nutrients. Proper hydration aids the body in retaining these minerals for better muscle function.
Cracks At Mouth Corners
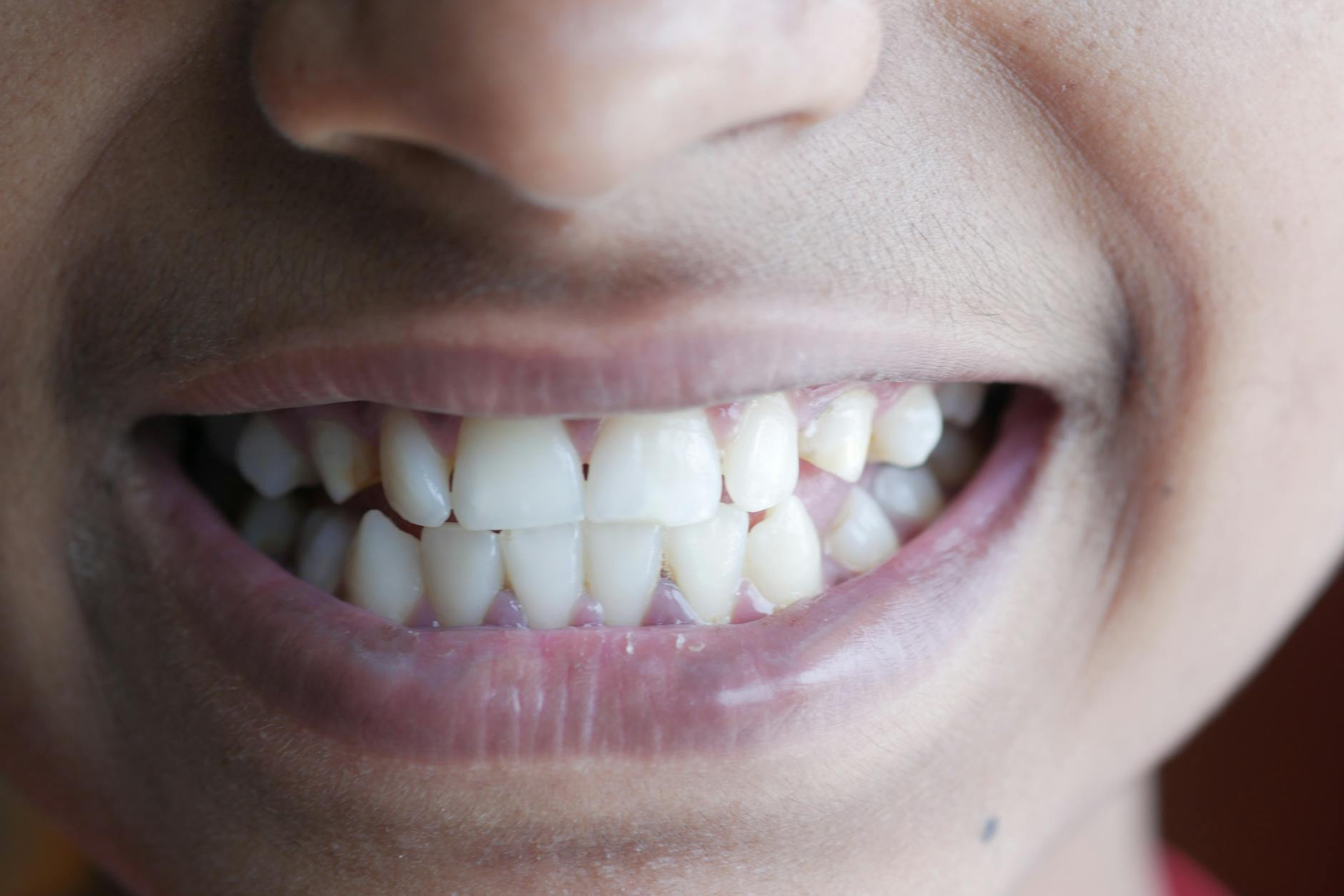
Angular cheilitis presents as painful inflammation and cracking at the corners of the lips. This condition usually results from insufficient riboflavin or iron in the daily diet. Saliva often gets trapped in the cracks and causes infection or fungal growth. The body struggles to repair the delicate skin in this area without adequate B vitamins. Consuming more poultry and salmon or broccoli helps heal the skin and prevent recurrence.
Chronic Fatigue

Feeling exhausted despite getting adequate sleep is a hallmark sign of anemia or B12 deficiency. The body relies on these nutrients to produce red blood cells that carry oxygen to tissues. A lack of oxygen delivery results in persistent lethargy and brain fog throughout the day. This type of tiredness does not resolve with caffeine or naps. Blood tests can easily confirm if nutrient levels are the root cause of the exhaustion.
Bone Pain

Deep aching in the bones frequently indicates a significant vitamin D deficiency. This nutrient is vital for calcium absorption and maintaining skeletal integrity. Adults with low levels often feel a general sense of soreness in their lower back or hips. Limited sun exposure and a diet low in fortified foods contribute to this widespread problem. Supplements are often necessary for those living in northern climates with less sunlight.
Slow Wound Healing
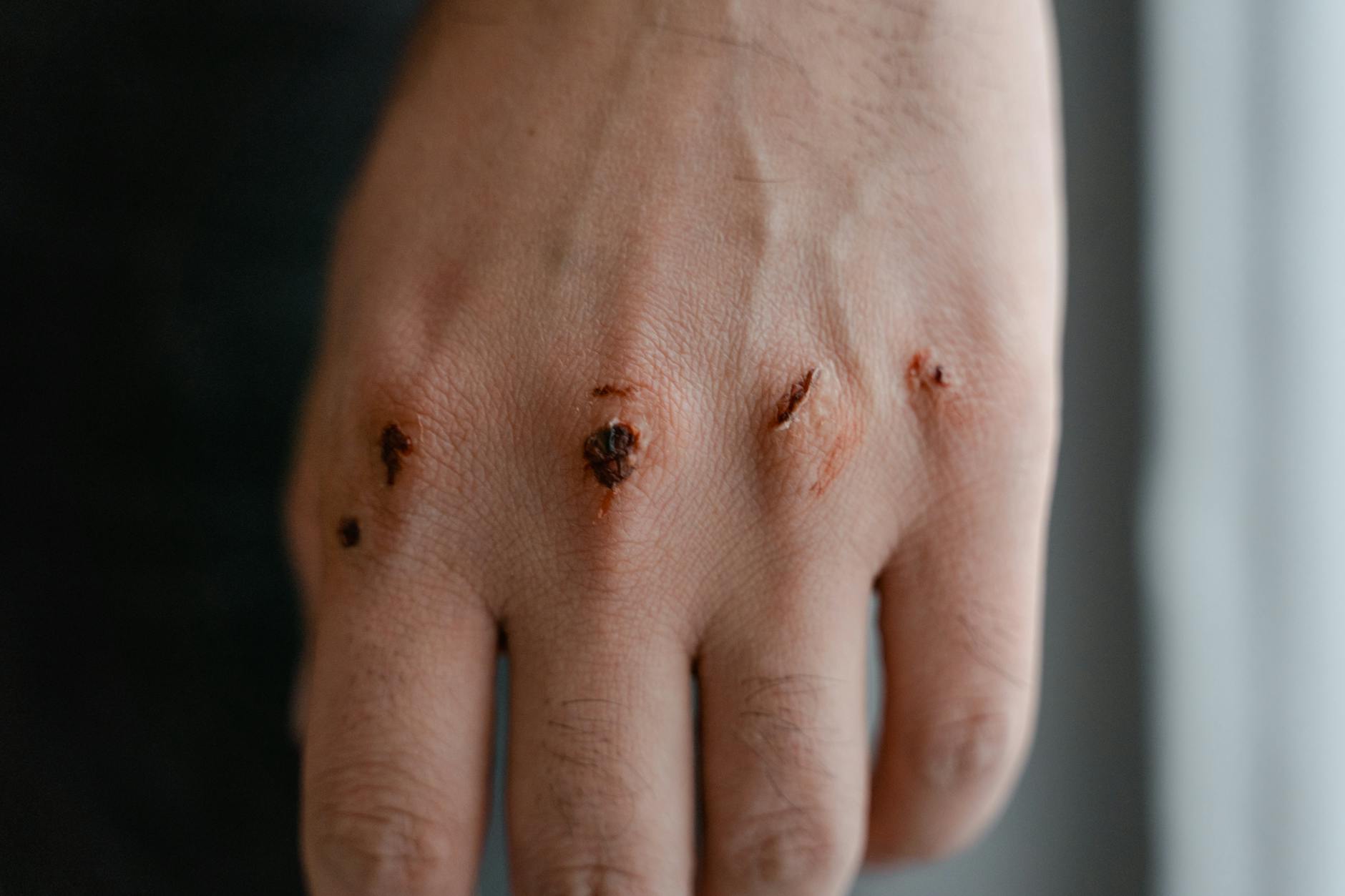
Cuts and scrapes that take weeks to heal often signal low vitamin C levels. Collagen production relies heavily on this vitamin to rebuild skin tissue after an injury. Without enough collagen the body struggles to close wounds and fight off potential infections. This issue becomes more prevalent in older adults or those with limited dietary variety. Increasing fruit and vegetable intake usually improves the speed of recovery.
Irregular Heartbeat
Palpitations or a skipping heartbeat can result from calcium or magnesium imbalances. These minerals regulate the electrical impulses that control the heart rhythm. Chronic deficiency puts stress on the cardiovascular system and requires medical attention. Stress often depletes magnesium stores and exacerbates the heart irregularities. Dietary adjustments involving nuts and seeds help stabilize these essential electrolyte levels.
Numbness In Extremities

Tingling sensations in the hands and feet often point to a lack of vitamin B12. This vitamin creates the protective sheath around nerves known as myelin. Damage to this sheath disrupts communication between the nerves and the brain. Vegans and vegetarians face a higher risk since B12 is found primarily in animal products. Fortified nutritional yeast or supplements provide a reliable alternative for plant-based eaters.
Pale Skin

A noticeable loss of color in the complexion often accompanies iron deficiency anemia. Hemoglobin gives blood its red color and skin its healthy pinkish hue. Low levels of hemoglobin cause the skin to appear washed out or sallow. This pallor can also affect the inside of the lower eyelids and the gum line. Iron-rich foods or supplements help restore healthy blood count and skin tone.
Depression And Mood Swings

Low levels of vitamin D and B vitamins frequently correlate with changes in mental health. The brain uses these nutrients to synthesize mood-regulating neurotransmitters like serotonin. Deficiencies can lead to feelings of sadness or irritability without an external cause. Many people notice these symptoms worsen during winter months when sunlight is scarce. Treating the nutritional gap often improves the effectiveness of other mental health therapies.
Shortness Of Breath

Feeling winded after minor exertion often indicates the body lacks iron. The heart and lungs must work harder to deliver oxygen when hemoglobin levels drop. This symptom can occur even in people who are otherwise physically fit. It serves as a warning sign that the body is running on empty reserves. Restoring iron levels typically resolves the breathing difficulties completely.
Cold Hands And Feet
Poor circulation resulting in cold extremities is a classic sign of anemia. The body prioritizes blood flow to vital organs when red blood cell counts are low. This survival mechanism leaves the hands and feet with less warmth and blood supply. The sensation persists even in warm environments or when wearing gloves. Addressing the underlying iron deficiency restores normal circulation patterns.
Weak Immune System

Frequent infections often suggest the body needs more vitamin C or zinc. These nutrients stimulate the production of white blood cells that fight off pathogens. A deficiency leaves the body vulnerable to viruses and bacteria in the environment. Recovery times from common colds extend significantly when nutrient stores are low. Daily intake of immune-boosting foods helps maintain a robust defense system.
Easy Bruising
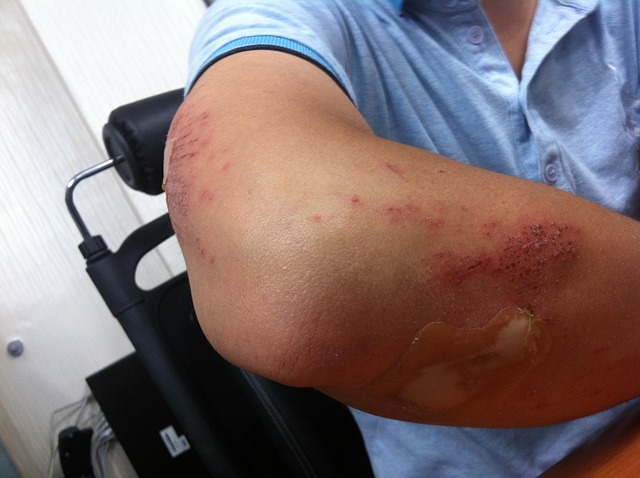
Appearing with mysterious bruises typically signals a lack of vitamin C or vitamin K. These vitamins are essential for blood clotting and maintaining strong blood vessel walls. Weak capillaries break easily under minor pressure and cause blood to pool under the skin. This issue is common in elderly individuals who may have restricted diets. Green leafy vegetables provide excellent sources for both of these critical nutrients.
Soft Or Brittle Bones

Osteomalacia involves the softening of bones due to severe vitamin D deficiency. This condition increases the risk of fractures from minor falls or injuries. The body leaches calcium from the skeleton when dietary intake is insufficient to maintain blood levels. This creates a porous structure that cannot support body weight effectively. Weight-bearing exercise and proper supplementation are key to reversing this decline.
Severe Dandruff

Flaking scalp skin often indicates a deficiency in zinc or B vitamins. These nutrients help metabolize fatty acids that keep the scalp hydrated and healthy. A lack of these elements leads to an overproduction of skin cells that shed visibly. Anti-dandruff shampoos only treat the symptom rather than the internal cause. Dietary improvements often clear up the flaking better than topical products.
Yellowish Skin Or Eyes

Jaundice can occur when vitamin B12 levels drop to a critically low point. The production of deformed red blood cells leads to their rapid breakdown in the liver. This process releases a byproduct called bilirubin which tints the skin and whites of the eyes yellow. This symptom requires immediate medical evaluation to rule out liver disease. B12 injections are often prescribed to correct the deficiency rapidly.
Brain Fog

Confusion and forgetfulness often accompany low levels of vitamin B12 or iron. The brain requires high amounts of oxygen and energy to process information efficiently. Deficiencies impair cognitive function and make concentration difficult. This mental cloudiness can affect work performance and daily tasks. Correcting the nutrient intake usually sharpens mental clarity and memory.
Red Swollen Tongue

Glossitis is a condition where the tongue becomes inflamed and appears smooth. This symptom strongly points to a lack of iron or B vitamins. The papillae on the tongue surface disappear and leave a painful and red appearance. Eating becomes difficult due to the tenderness and sensitivity to spices. Nutritional therapy restores the normal texture and color of the tongue.
White Spots On Nails
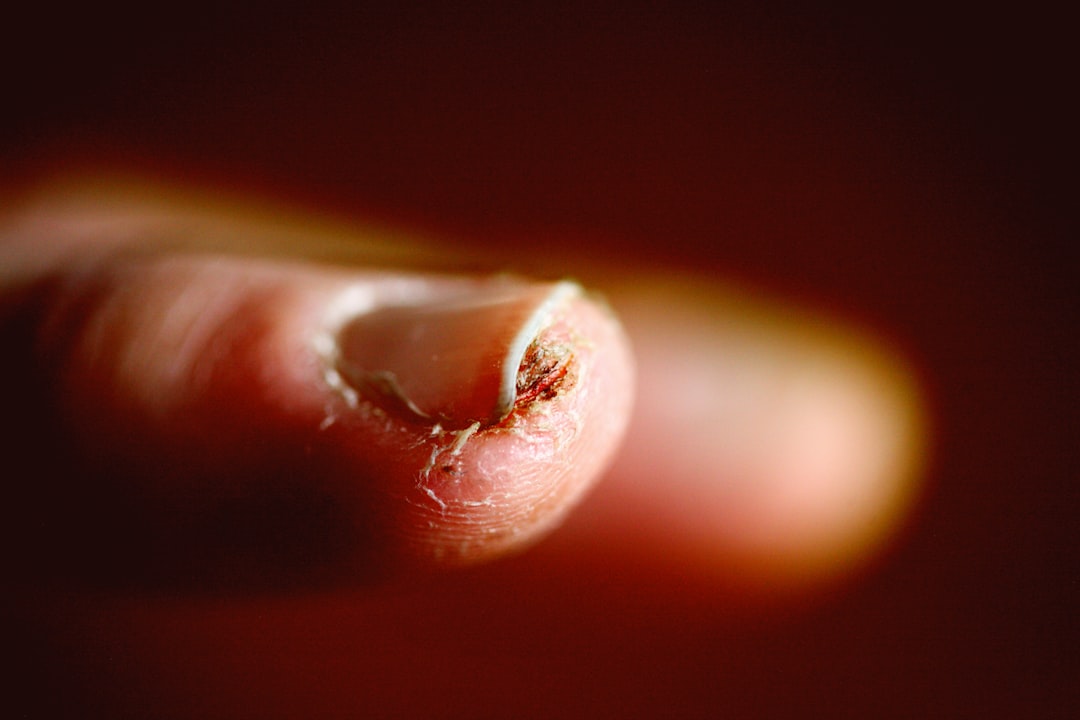
Small white marks on fingernails are often attributed to zinc deficiency. While injury can cause them the persistence of spots suggests a nutritional gap. Zinc plays a major role in cell division and protein synthesis needed for nail growth. The spots typically grow out as the nail lengthens over time. Oysters and pumpkin seeds are potent sources of zinc to clear up this cosmetic issue.
Excessive Sweating

Head sweating specifically can be an early sign of a vitamin D deficiency. This symptom is often subtle and attributed to room temperature or physical exertion. Neuromuscular irritability caused by low vitamin D triggers overactive sweat glands. This presentation is more common in infants but affects adults as well. Checking vitamin D levels is a simple step for those experiencing unexplained perspiration.
Dry Eyes

Chronic dryness and the inability to produce tears point to a vitamin A deficiency. The eyes depend on this vitamin to maintain the tear film and protect the cornea. Without it the eyes feel gritty and become sensitive to light. Long-term dryness can lead to scarring and vision impairment. Liver and dairy products provide high amounts of preformed vitamin A.
Persistent Acne

Skin that refuses to clear up may be signaling low levels of zinc or vitamin A. These nutrients reduce inflammation and regulate the production of sebum. A deficiency allows oil to clog pores and bacteria to flourish on the skin. Hormonal acne often responds well to zinc supplementation. A diet focused on anti-inflammatory foods supports clearer skin from the inside out.
Nosebleeds

Frequent and spontaneous nosebleeds often result from a vitamin K deficiency. This vitamin is the primary agent responsible for the blood clotting cascade. Without adequate levels even minor dryness or bumps can cause prolonged bleeding. The body cannot synthesize enough clotting factors to stop the flow quickly. Leafy greens and fermented foods are the best natural sources of vitamin K.
Dizziness

Feeling lightheaded upon standing typically indicates low iron or B12. The brain experiences a temporary drop in oxygen due to insufficient red blood cells. This sensation creates instability and can lead to fainting spells. It serves as an immediate signal that blood volume or quality is compromised. Hydration helps but nutrient restoration is the permanent fix.
Neck Swelling

A visible enlargement at the base of the neck suggests an iodine deficiency. The thyroid gland swells in an effort to trap more iodine from the bloodstream. This condition is known as a goiter and affects metabolism significantly. Iodized salt was introduced specifically to combat this public health issue. Seafood and dairy are also natural sources of this essential trace mineral.
Constipation

Irregular bowel movements frequently stem from a lack of magnesium. This mineral relaxes the muscles in the intestines to allow for smooth passage of waste. It also draws water into the colon to soften the stool. Chronic deficiency leads to hard stools and discomfort. Magnesium citrate is a common remedy used to restore regularity.
Severe PMS Symptoms

Intense cramping and mood swings often correlate with low calcium and magnesium. These minerals help regulate muscle contractions and nerve signaling during the menstrual cycle. Deficiencies exacerbate pain and water retention significantly. Studies show that increasing intake reduces the severity of monthly symptoms. Yogurt and leafy greens are excellent additions to the diet for relief.
Share your thoughts on which signs you have noticed in your own life in the comments.





