Metabolic health dictates how efficiently your body converts food into energy and manages essential biological functions throughout the day. A slowing metabolism often manifests through subtle physical and mental cues that are easy to dismiss as simple signs of aging or stress. Recognizing these symptoms early allows for lifestyle adjustments that can reignite metabolic fire and prevent long-term health complications. The following indicators suggest your internal engine might be decelerating more rapidly than the standard physiological baseline.
Unexplained Weight Gain

You might notice the number on the scale creeping up despite maintaining your usual diet and exercise habits. This phenomenon suggests your body is no longer burning calories as efficiently as it once did during daily activities. Fat accumulation often targets the midsection or hips when the metabolic rate takes a significant downward turn. It serves as a frustrating indicator that your basal energy expenditure has dropped below your caloric intake. Monitoring this subtle shift is crucial for catching metabolic slowdowns before they become major health hurdles.
Chronic Fatigue
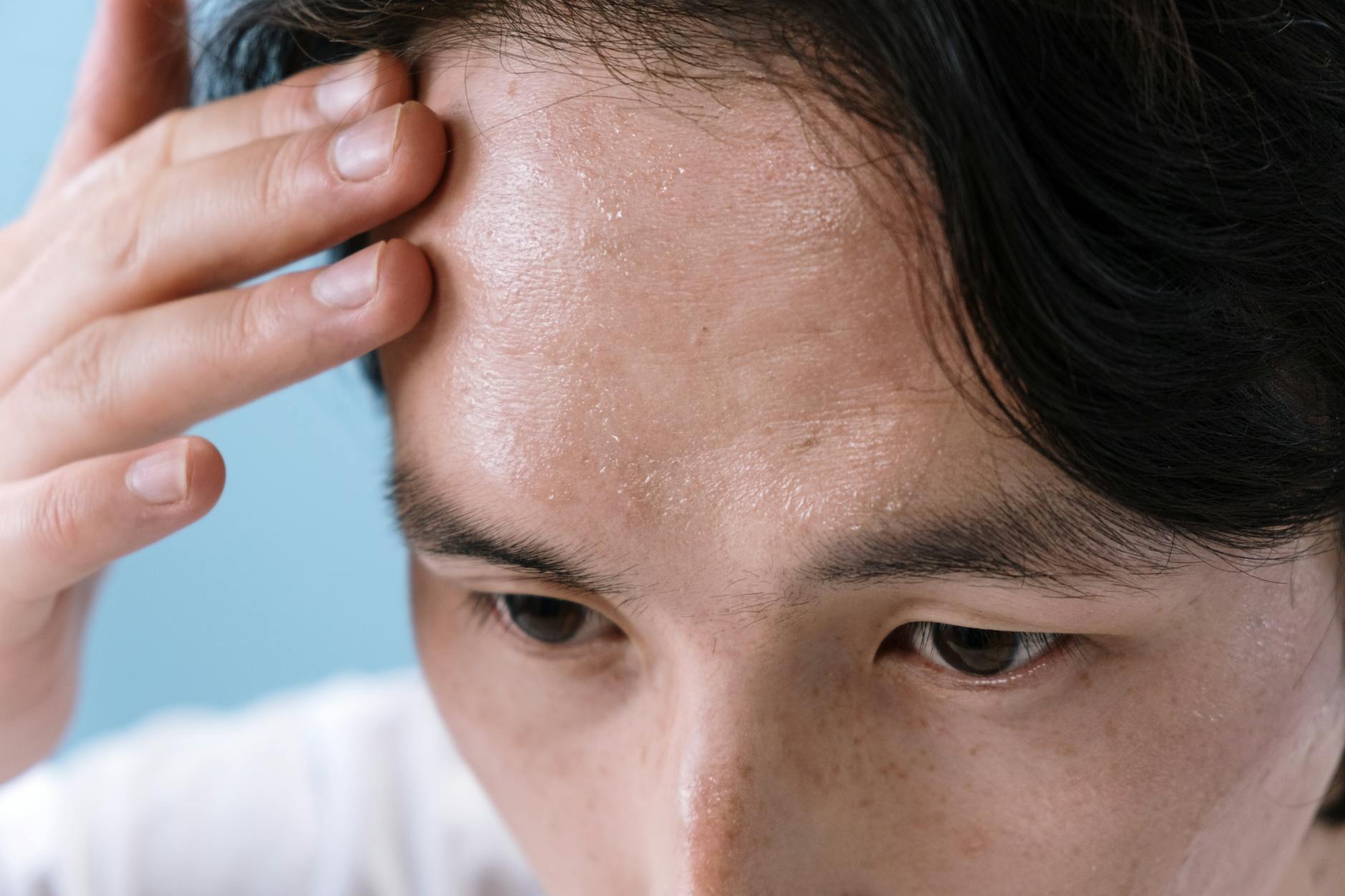

Waking up tired even after a full night of sleep is a classic red flag for metabolic sluggishness. Your body struggles to convert nutrients into usable fuel which leaves you feeling drained and lethargic. This exhaustion often persists throughout the day and resists the temporary boost usually provided by caffeine or sugar. A persistent lack of energy impacts physical performance and reduces your overall motivation to stay active. It indicates that your cellular energy production processes are not operating at optimal levels.
Constant Coldness

Feeling chilly when everyone else in the room is comfortable points directly to a reduction in heat generation. Your metabolism generates body heat as a byproduct of burning calories and keeping your systems running. When this process slows down your body prioritizes keeping vital organs warm by reducing blood flow to the extremities. You may find yourself reaching for a sweater or blanket even during relatively mild weather conditions. This symptom highlights a decrease in thermogenesis which is a key component of a healthy metabolic rate.
Hair Thinning
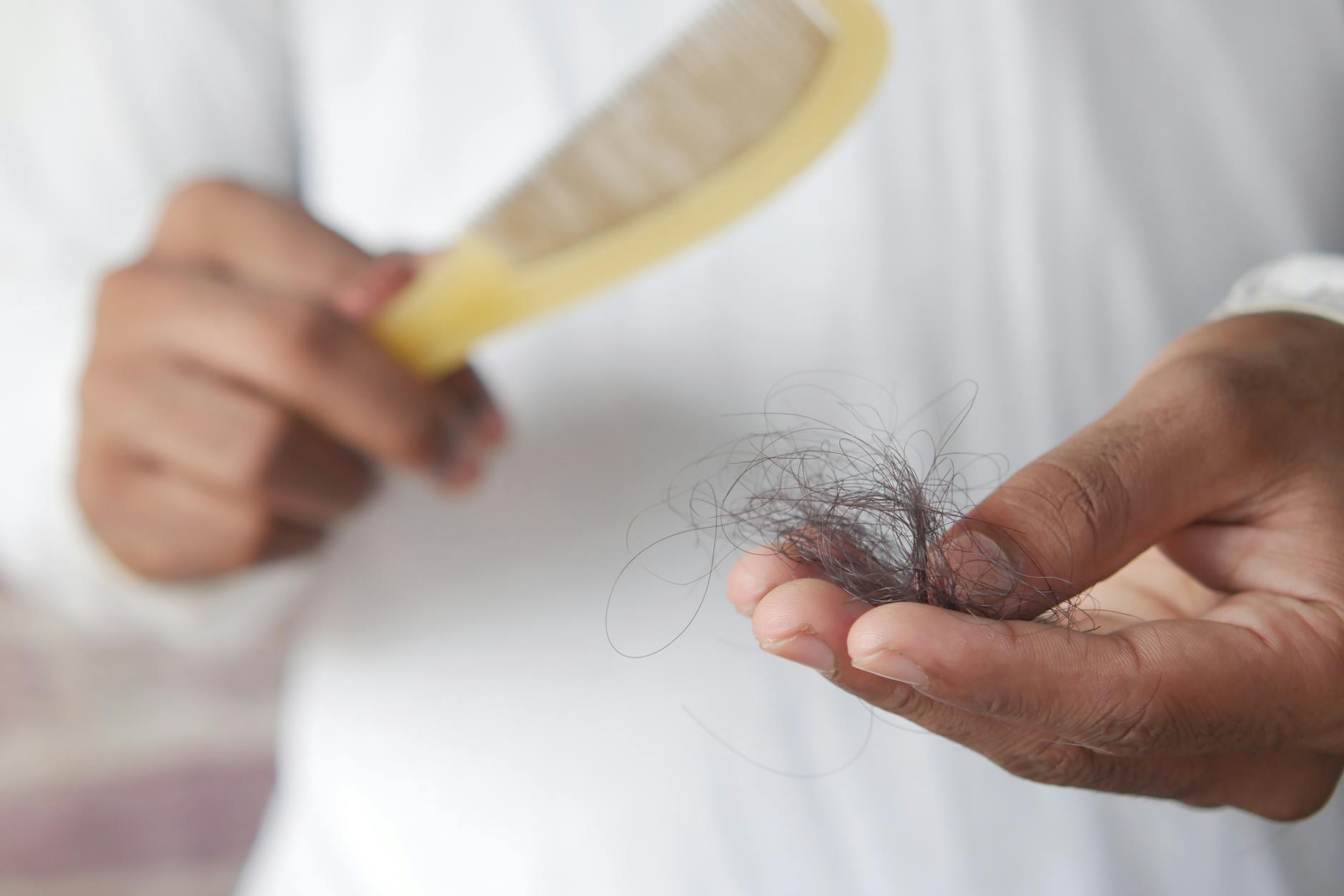

Hair follicles require a significant amount of energy to sustain growth and regeneration cycles. A sluggish metabolism diverts resources away from non-essential functions like hair maintenance to preserve energy for vital organs. You might notice more strands in the shower drain or a general loss of volume over several months. This shedding often occurs because the body is in a state of energy conservation rather than growth. Restoring metabolic balance is often necessary to revive the health and thickness of your hair.
Dry And Cracked Skin
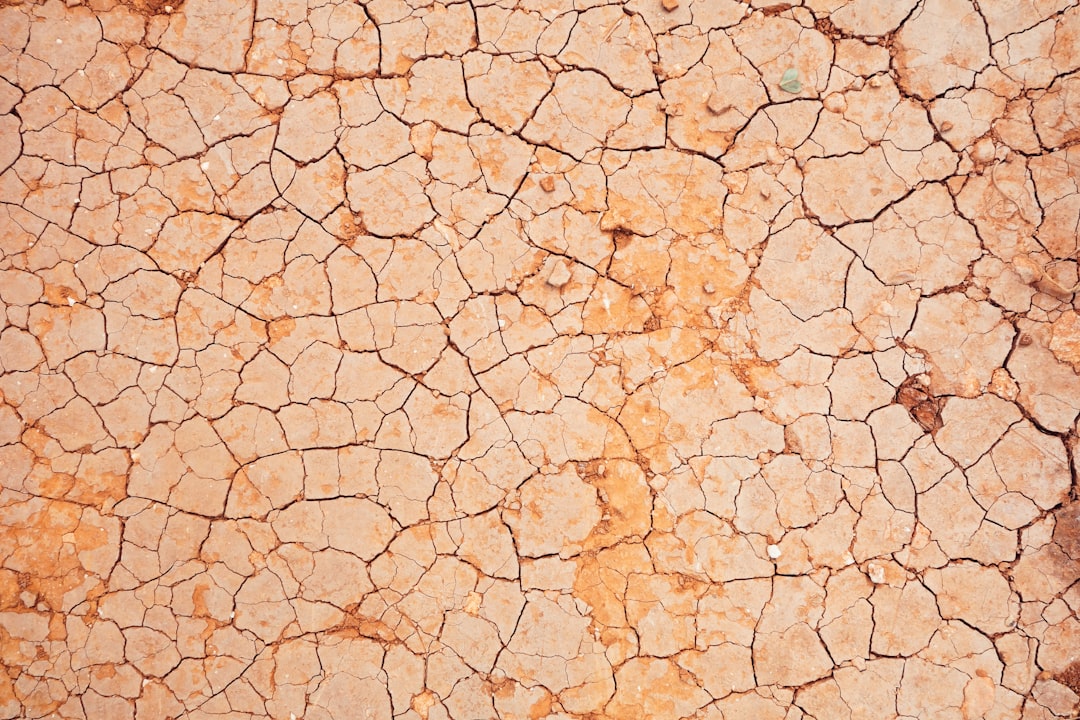

Your skin relies on a steady supply of nutrients and proper blood flow to stay hydrated and elastic. A slower metabolism reduces circulation and delays the delivery of essential moisture to the skin surface. You may experience flakiness or a dull complexion that does not improve with topical moisturizers alone. This lack of vitality in the skin barrier reflects internal inefficiencies in processing fats and hydration. Addressing the root metabolic cause can often restore the natural glow and texture of the skin.
Brittle Nails
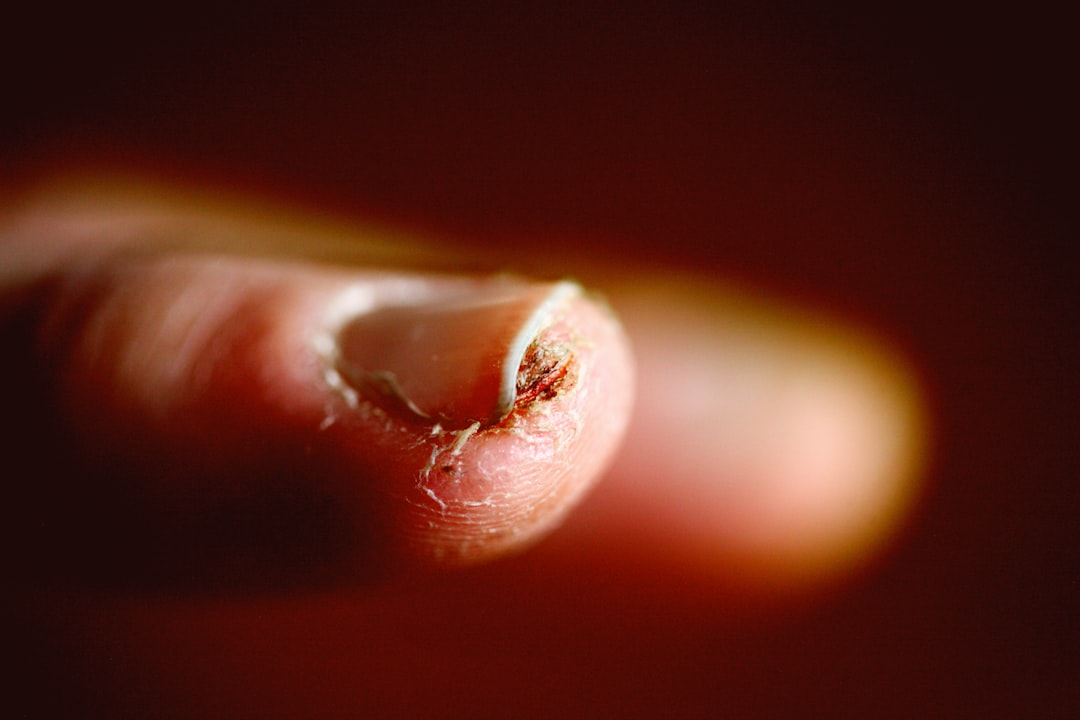
Nails that break or split easily often signal a lack of necessary nutrients reaching the nail bed. Slow metabolic processes impair the absorption and distribution of proteins and minerals required for strong nail plates. You might observe vertical ridges or a lack of the usual smooth surface on your fingernails. This fragility serves as an external sign that your body is conserving energy by limiting peripheral growth. Strengthening the nails often requires boosting internal metabolic function rather than just applying hardeners.
Sugar Cravings

intense desire for sweets indicates your body is desperate for a quick energy fix due to inefficient fuel processing. When metabolism slows down your cells may not be receiving glucose effectively which triggers hunger signals. These cravings often lead to a cycle of energy spikes and crashes that further disrupt metabolic rhythm. Relying on sugar for energy creates insulin spikes that can exacerbate the underlying issue of metabolic slowdown. Breaking this cycle requires stabilizing blood sugar through balanced nutrition and metabolic support.
Difficulty Concentrating

Brain fog and an inability to focus are frequently linked to how well your brain receives energy from glucose. A slow metabolism can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar levels that impair cognitive function and mental clarity. You may find it harder to complete complex tasks or remember small details throughout the work day. This mental sluggishness suggests that your brain is not getting the steady fuel supply it needs to perform optimally. Sharpening your mind often involves addressing the metabolic inefficiencies causing these energy dips.
Afternoon Energy Crashes
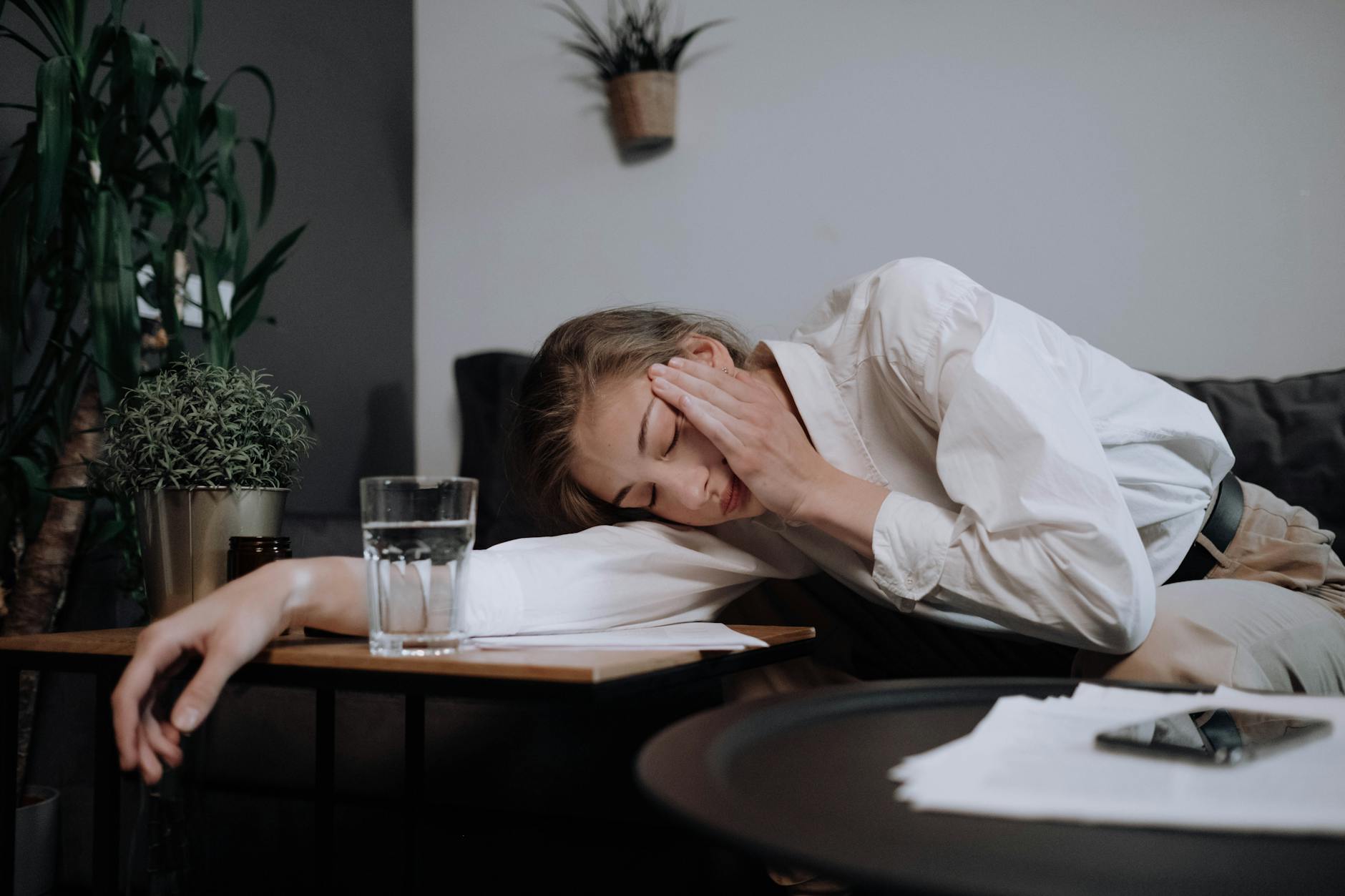

Hitting a wall of exhaustion around mid-afternoon is a common symptom of metabolic instability. This slump typically occurs when your body struggles to sustain energy levels after the lunchtime digestive process. You might feel an overwhelming urge to nap or require stimulants to power through the rest of the day. It indicates that your metabolism is having trouble maintaining a consistent energy output over extended periods.Smoothing out these peaks and valleys requires a focus on metabolic consistency and nutrient timing.
Constipation

A slower metabolism impacts the speed at which food moves through your digestive tract. Peristalsis or the wave-like muscle contractions that move waste can become sluggish and lead to irregularity. You may experience less frequent bowel movements or general digestive discomfort as a result. This internal stagnation allows toxins to remain in the system longer and reabsorb into the bloodstream. improving digestive transit time is often linked to speeding up overall metabolic rate.
Low Libido
Reproductive hormones are closely tied to metabolic health and overall energy availability. When your body enters a state of energy conservation it often downregulates reproductive drive to save resources. You might notice a significant drop in sexual desire that does not correlate with other life stressors. This reduction in libido serves as a biological signal that the body is prioritizing survival over reproduction. Restoring hormonal balance typically requires addressing the underlying metabolic slowdown.
Mood Swings

Fluctuations in blood sugar and energy levels can wreak havoc on your emotional stability. A slow metabolism often leads to irritability and anxiety as the brain struggles with inconsistent fuel. You may find yourself snapping at loved ones or feeling weepy without a clear external trigger. These mood disturbances are often a direct result of the physiological stress caused by metabolic inefficiency. Stabilizing your metabolism can act as a powerful tool for regulating emotional health.
Insomnia

Metabolic issues can disrupt the delicate balance of hormones like cortisol and melatonin that regulate sleep. You might find yourself waking up frequently during the night or struggling to fall asleep despite being tired. Poor sleep quality further depresses the metabolism creates a vicious cycle of fatigue and dysfunction. This inability to rest deeply prevents the body from performing essential repair work during the night. addressing metabolic health is often the key to unlocking restorative sleep patterns.
Severe Headaches
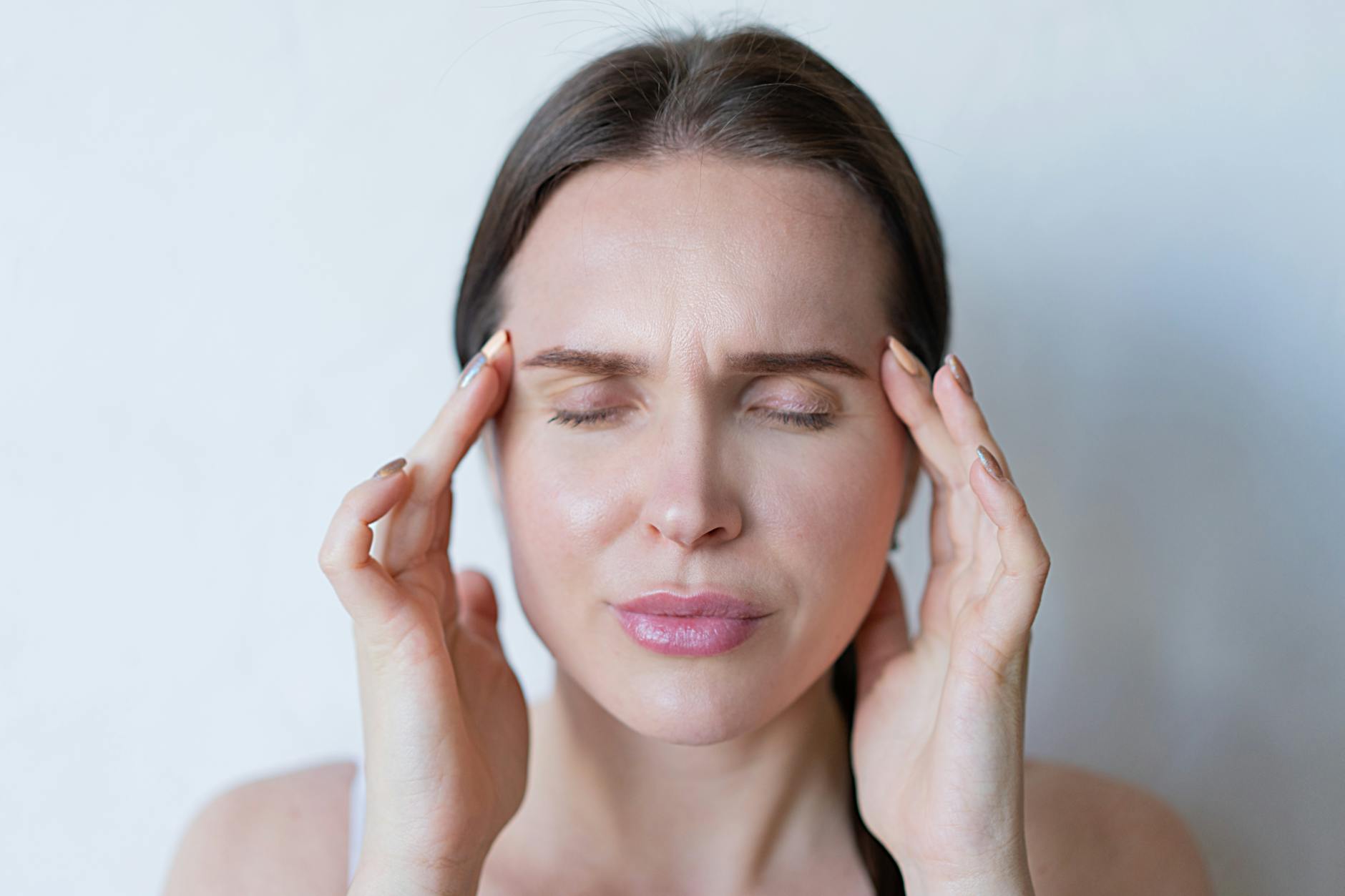

Frequent headaches can stem from blood sugar imbalances or hormonal shifts caused by a sluggish metabolism. Your brain is highly sensitive to changes in glucose levels and can react with pain when supply is inconsistent. You might experience throbbing tension that does not respond well to standard hydration or pain relievers. These headaches serve as a warning that your neurological system is under stress from metabolic strain. deeply ingrained metabolic issues often present as chronic tension or migraines.
Bloating After Meals
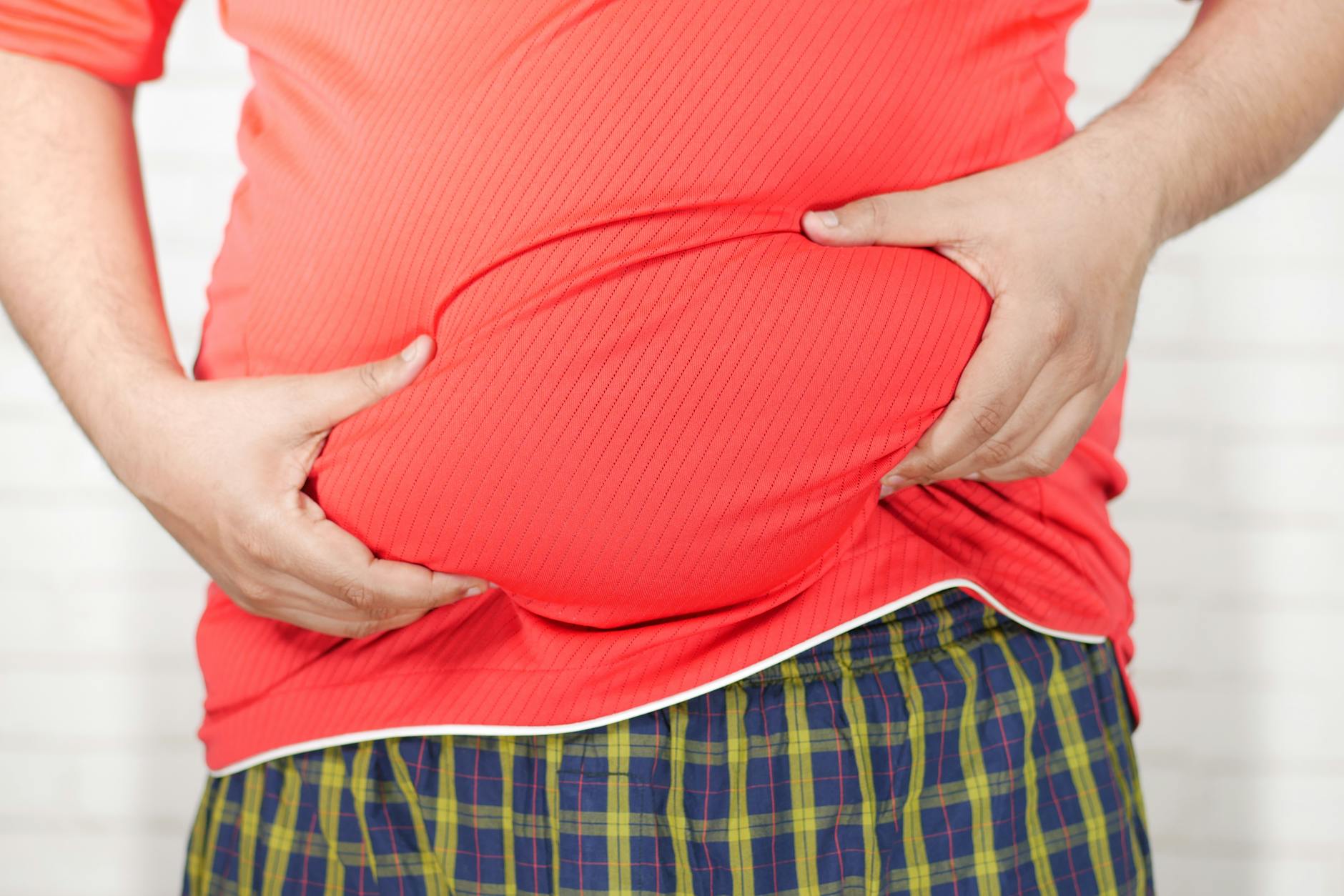

Digestive inefficiency often leads to fermentation in the gut which produces excess gas and bloating. When metabolism slows down the enzymes required to break down food may not function at full capacity. You may feel uncomfortably full even after eating a relatively small or light meal. This distention indicates that your digestive fire is weak and struggling to process nutrients. resolving this discomfort usually involves boosting digestive and metabolic capability.
Cold Hands And Feet
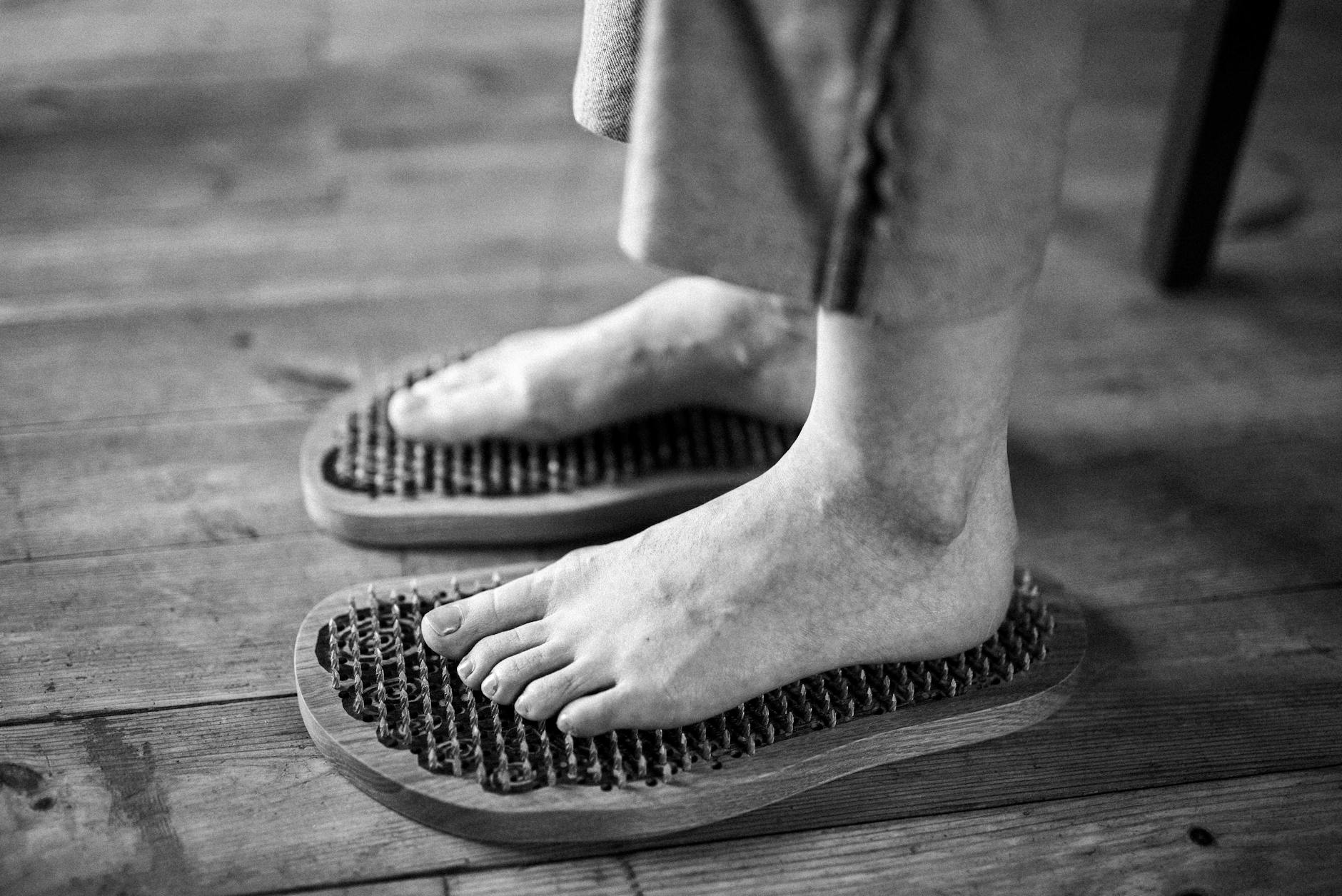

Circulation often suffers when the metabolism slows down as the body conserves heat for the core. You might notice that your extremities remain icy even when you are wearing warm socks or gloves. This symptom suggests that blood flow is being restricted to the periphery to maintain internal temperature. It is a survival mechanism that indicates your basal metabolic rate is lower than optimal. Warming up the metabolism can help restore proper circulation to fingers and toes.
Joint Pain
Systemic inflammation is often elevated when metabolic processes are not clearing waste products efficiently. You may experience stiffness or aching in your joints that mimics the symptoms of arthritis. This discomfort can deter physical activity which further slows down the metabolism in a negative feedback loop. The accumulation of inflammatory markers is a sign that the body’s repair mechanisms are sluggish. reducing this inflammation requires a comprehensive approach to metabolic healing.
Muscle Weakness

A body in energy conservation mode may begin to catabolize muscle tissue for fuel. You might notice that lifting heavy objects feels more difficult or that your gym performance is plateauing. This loss of strength occurs because the body is not synthesizing protein efficiently to repair muscle fibers. It is a critical sign that your metabolism is prioritizing immediate energy needs over tissue maintenance. rebuilding strength requires signaling the body that it has enough energy to support muscle growth.
High Cholesterol

Metabolism plays a key role in processing lipids and managing cholesterol levels in the bloodstream. A slowdown can lead to an accumulation of LDL cholesterol as the body fails to clear it effectively. You may receive unexpected blood test results despite following a generally heart-healthy diet. This internal marker indicates that lipid metabolism is not functioning at the speed required for optimal health. dietary changes alone may not suffice without addressing the metabolic root.
Increased Cellulite

Changes in the structure of the skin and underlying fat can become more pronounced with a slow metabolism. You might notice more dimpling on the thighs and buttocks as connective tissue weakens and fat cells enlarge. This aesthetic change reflects poor circulation and lymphatic drainage in the affected areas. It suggests that the body is struggling to mobilize fat stores and maintain tissue elasticity. improving metabolic rate can help smooth the appearance of the skin over time.
Irregular Periods

Hormonal imbalances resulting from metabolic stress often disrupt the menstrual cycle. You may experience cycles that are longer or shorter than usual or periods that are exceptionally heavy or light. This irregularity signals that the reproductive system is under strain due to energy conservation. It is a protective mechanism where the body deems conditions unfavorable for potential pregnancy. restoring regularity often depends on fixing the underlying metabolic health.
High Blood Pressure
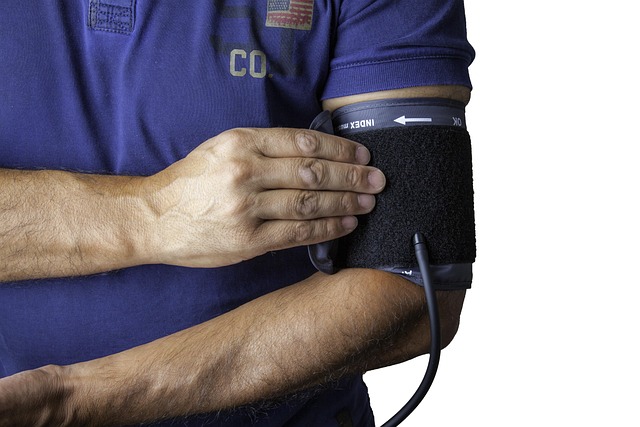
Metabolic syndrome often includes hypertension as the body struggles to regulate fluid balance and vessel tone. You might see your blood pressure reading inching up during routine checkups without a clear cause. This increase puts additional strain on the heart and cardiovascular system over time. It indicates that the mechanisms controlling blood volume and resistance are compromised. managing metabolism is a crucial step in maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.
Intense Carb Cravings

A specific hunger for bread and pasta points to a body that is having trouble accessing stored fat for fuel. You might feel unsatisfied after meals unless they contain a significant amount of starch. This dependency on dietary glucose indicates metabolic inflexibility or the inability to switch between fuel sources. It traps the body in a cycle of relying on frequent carbohydrate intake to function. breaking this dependence requires training the metabolism to burn fat efficiently.
Excessive Thirst

Metabolic imbalances can affect how the body manages fluids and electrolytes. You might find yourself drinking water constantly but still feeling parched or dehydrated. This symptom can sometimes be a precursor to blood sugar issues related to metabolic slowdown. It suggests that your cellular hydration processes are not working as they should. monitoring thirst levels can provide insight into your internal chemical balance.
Slow Wound Healing
The body requires energy and protein synthesis to repair cuts and scrapes effectively. A sluggish metabolism delays the delivery of these essential repair materials to the injury site. You may notice that minor scratches take weeks to disappear rather than days. This slow recovery rate indicates that the body’s regenerative capabilities are dampened. boosting metabolic function can accelerate the natural healing process.
Depression

The gut-brain connection means that metabolic health has a profound impact on mental well-being. A slow metabolism can reduce the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine. You might experience persistent feelings of sadness or hopelessness that seem disconnected from life events. This biochemical imbalance highlights the link between physical energy production and emotional state. treating the whole body is often necessary to lift the mental fog.
Anxiety

Physical stress from metabolic dysregulation often manifests as psychological anxiety. You might feel a constant underlying sense of dread or nervousness without a specific cause. This state of high alert is often driven by fluctuating blood sugar and cortisol levels. It indicates that the body feels unsafe due to unstable energy availability. stabilizing the metabolism can have a calming effect on the nervous system.
Reduced Sweating

Sweating is a natural cooling mechanism that requires a robust metabolic response to exercise or heat. You might notice that you hardly break a sweat even during intense physical exertion. This lack of perspiration suggests that your body is not generating enough heat to trigger the cooling process. It points to a lowered metabolic rate that is conserving resources rather than expending them. healthy sweating is a sign of an active and responsive metabolism.
Thinning Eyebrows
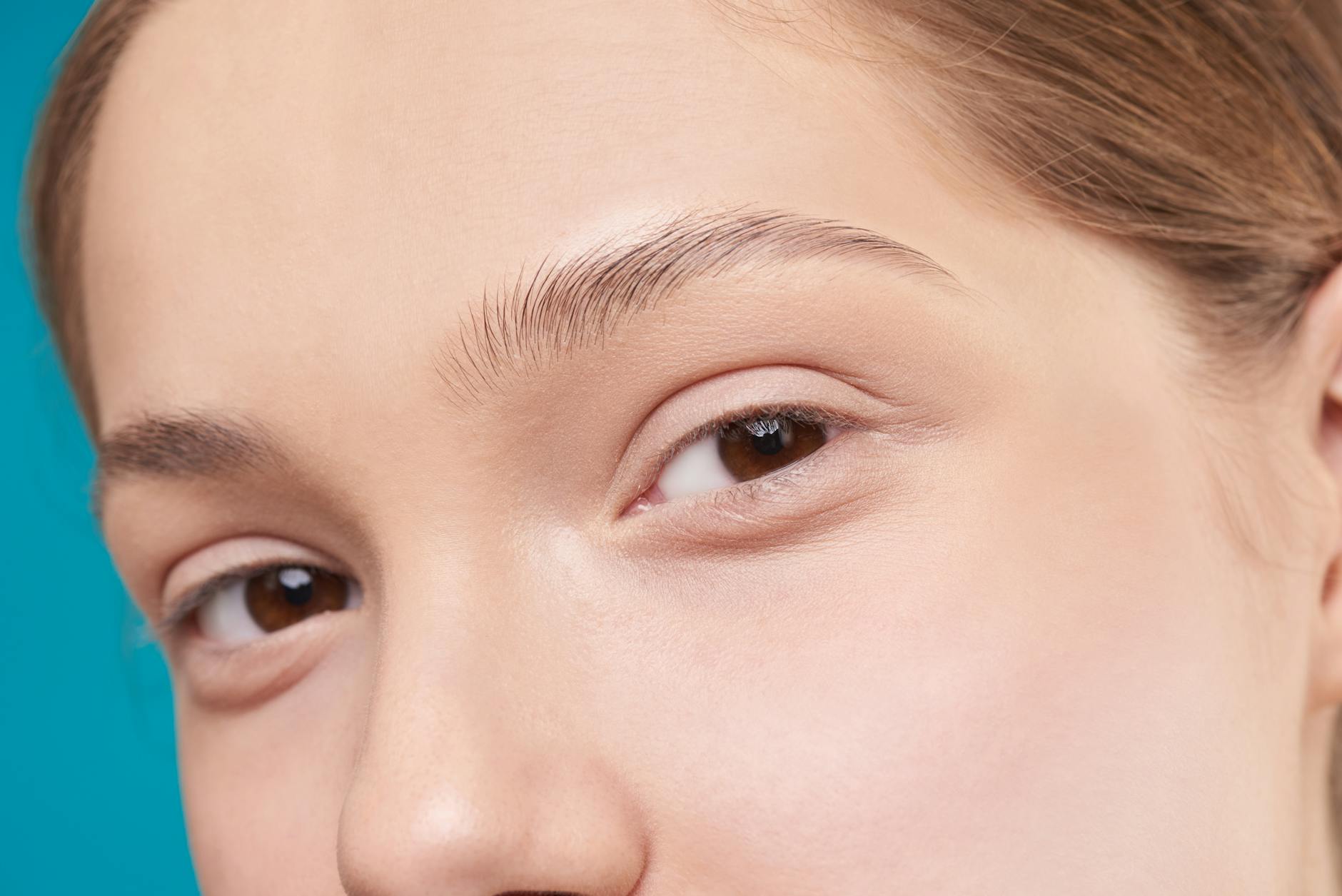

Losing the outer third of the eyebrows is a specific sign often linked to thyroid function and metabolic rate. You might notice that your brows look shorter or sparser than they did in previous years. This distinct pattern of hair loss serves as a clinical clue for hormonal slowing. It indicates that the thyroid gland may not be producing enough hormones to drive metabolism. addressing thyroid health is essential for reversing this symptom.
Puffy Face
Fluid retention in the face is common when the metabolism is not clearing waste fluids efficiently. You might wake up with swollen eyes or a rounder face that does not subside quickly. This puffiness reflects a sluggish lymphatic system and poor kidney filtration rates. It suggests that the body is holding onto water to dilute toxins or manage inflammation. lymphatic support can help reduce this visible sign of slowdown.
Memory Lapses

Forgetfulness is another cognitive symptom that arises when the brain lacks consistent energy. You might walk into a room and forget why you are there or struggle to recall names. These minor lapses indicate that the neurons are not firing with optimal speed or connectivity. It serves as a sign that metabolic support is needed to preserve cognitive sharpness. feeding the brain with stable energy helps improve memory retention.
Heart Palpitations
Irregular heartbeats can occur when electrolyte balances and energy signals are disrupted. You might feel your heart fluttering or skipping a beat during moments of rest. This sensation can be alarming and is often linked to the stress of a struggling metabolism. It indicates that the autonomic nervous system is firing somewhat erratically. calming the metabolic system can often resolve these benign arrhythmias.
Acid Reflux

Low stomach acid is frequently associated with a slow metabolism and can paradoxically cause heartburn. You may experience burning sensations because food is sitting in the stomach too long without being digested. This delay creates upward pressure that forces acid into the esophagus. It signals that the digestive fires need to be stoked rather than suppressed. improving stomach acid production is key to better digestion and metabolism.
Weak Immune System

A body that is conserving energy will often downregulate immune function as a non-essential survival trade-off. You might catch colds more frequently or struggle to shake off minor infections. This susceptibility indicates that your white blood cells are not getting the support they need. It serves as a warning that your overall vitality is compromised by a slow metabolism. strengthening metabolic health builds a more robust defense against illness.
Difficulty Building Muscle

Even with dedicated strength training you may find it nearly impossible to add muscle mass. This resistance occurs because the anabolic processes required for growth are stalled. You might see zero gains despite lifting heavy and eating protein. It indicates that your body refuses to allocate energy to building new tissue. unlocking muscle growth potential requires a metabolic reset.
We invite you to detail your own experiences with these signs in the comments.





