Excessive sugar consumption often manifests through various physical signals that the body sends to indicate an imbalance. These warnings can range from subtle skin changes to significant fluctuations in energy levels throughout the day. Recognizing these symptoms allows individuals to adjust their dietary habits and restore their overall well-being. A diet high in processed sugars impacts multiple systems including digestion and cognitive function. Paying attention to these physical cues helps in maintaining long-term health and preventing chronic conditions.
Constant Fatigue

Feeling tired all the time is a common indicator that your diet may contain too much sugar. High insulin levels cause blood sugar to spike and then crash rapidly. This rollercoaster effect leaves the body feeling drained and lethargic shortly after eating. Reliance on sweet snacks for energy often perpetuates this cycle of exhaustion.
Frequent Acne Breakouts
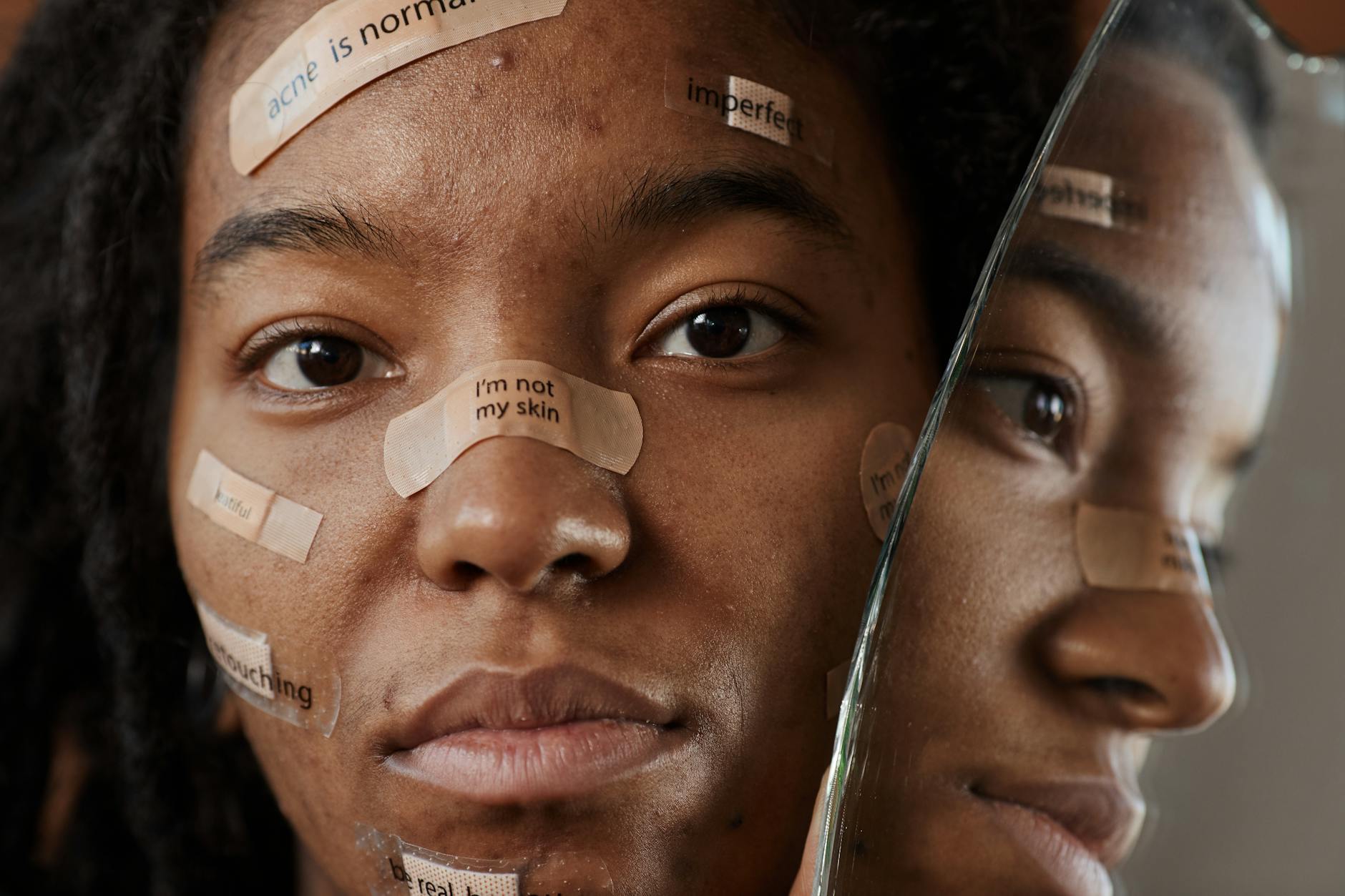

Systemic inflammation caused by high sugar intake can lead to skin issues like acne. Sugar spikes insulin levels which in turn increases oil production in the skin. This excess oil clogs pores and creates an environment where bacteria can thrive. Reducing sugar consumption often results in a clearer and more radiant complexion over time.
Unexplained Weight Gain

Consuming excess sugar adds empty calories that do not provide satiety or essential nutrients. The body converts this surplus glucose into fat cells for storage. High insulin levels also block the body from using stored fat as energy. This process often leads to gradual weight gain without a significant change in other lifestyle factors.
Intense Sweet Cravings

Eating sugar releases dopamine in the brain and creates a reward loop that demands more stimulation. The more sugar you consume the more your body craves it to maintain that chemical high. This dependency makes it difficult to feel satisfied with whole foods. Breaking this cycle usually requires a period of strict reduction to reset the palate.
Irritable Mood Swings

Rapid fluctuations in blood sugar levels directly impact brain function and emotional stability. A sudden drop in glucose can cause irritability and anxiety or even depressive symptoms. These mood swings are often described as being hangry when meals are delayed. Stable blood sugar is essential for maintaining a balanced and calm emotional state.
Tooth Decay and Cavities
Bacteria in the mouth feed on sugar and produce acid as a byproduct. This acid erodes tooth enamel and eventually leads to cavities and decay. Frequent consumption of sugary drinks or sticky sweets increases the duration of this acid attack. Good oral hygiene cannot fully counteract the damage caused by a constant supply of sugar.
Joint Pain and Inflammation

Sugar is a known inflammatory agent that can exacerbate pain in the joints and muscles. Chronic inflammation causes stiffness and aches that may be mistaken for aging or arthritis. Reducing sugar intake can significantly lower inflammatory markers in the body. Many people experience improved mobility and less pain after cutting out processed sweets.
Premature Skin Aging

A process called glycation occurs when excess sugar attaches to proteins in the bloodstream. This process damages collagen and elastin which keep skin firm and youthful. The result is the premature appearance of wrinkles and sagging skin. Limiting sugar helps protect these structural proteins and maintains skin elasticity.
Digestive Bloating

Bad bacteria and yeast in the gut ferment sugar and produce gas as a result. This fermentation process leads to uncomfortable bloating and flatulence after meals. An imbalance in gut flora can also cause irregular bowel movements. Restoring gut health often begins with starving these harmful organisms of their preferred food source.
Elevated Blood Pressure
High insulin levels can cause blood vessels to retain more sodium and fluid. This retention increases the volume of blood and raises blood pressure levels. The added strain on the heart and arteries contributes to cardiovascular risks. reducing sugar intake is often a recommended strategy for managing hypertension naturally.
Persistent Brain Fog

Glucose creates bursts of energy but creates cognitive crashes shortly after. High blood sugar can damage blood vessels in the brain and reduce cognitive efficiency. This often manifests as difficulty concentrating or remembering names and details. A low-sugar diet supports clearer thinking and better mental focus throughout the day.
Disrupted Sleep Patterns

Eating sugary foods late in the day can overstimulate the body and make it hard to fall asleep. The subsequent blood sugar crash during the night may cause waking or restless sleep. Poor sleep quality then increases cravings for sugar the next day. This creates a negative feedback loop that harms overall rest and recovery.
Weakened Immune System

Sugar temporarily impairs the ability of white blood cells to destroy bacteria and viruses. This suppression can last for several hours after consuming a sugary meal. A diet high in sugar leaves the body more susceptible to infections and illnesses. Reducing intake supports the immune system in fighting off common colds and flu.
Excessive Thirst

When there is too much sugar in the blood the kidneys work harder to filter it out. This process pulls fluids from tissues and leads to frequent dehydration. The body signals this dehydration through an intense feeling of thirst. Drinking sugary beverages to quench this thirst only exacerbates the problem.
Frequent Urination

The kidneys attempt to flush out excess sugar by producing more urine. This diuretic effect forces you to visit the restroom more often than usual. It is a direct response to the body trying to balance high glucose levels. This symptom is often one of the earliest warning signs of blood sugar issues.
Dry and Itchy Skin
High blood sugar can damage nerves and cause loss of body fluids. This dehydration affects the skin and makes it feel dry or itchy. Essential oils in the skin are depleted more rapidly when glucose levels are elevated. Using moisturizer may not be enough if the underlying dietary cause is not addressed.
Recurring Headaches

Fluctuations in blood sugar can trigger headaches or migraines in sensitive individuals. The rapid expansion and contraction of blood vessels play a role in this pain. Dehydration caused by sugar metabolism also contributes to head pain. Stabilizing glucose levels is a key step in preventing these dietary headaches.
Frequent Yeast Infections
Yeast thrives on sugar and grows rapidly when it is available in abundance. High sugar intake creates the perfect environment for candida to multiply. This can lead to recurring infections in various parts of the body. dietary changes are often necessary to bring yeast populations back under control.
Increased Anxiety Levels

The physical symptoms of a sugar crash often mimic a panic attack. Shaking and a racing heart can induce feelings of anxiety and nervousness. The brain interprets these physiological stress signals as emotional distress. stabilizing blood sugar helps mitigate these chemically induced feelings of panic.
Gum Disease

Sugar promotes the growth of bacteria that cause gum inflammation and bleeding. Chronic high blood sugar also weakens the immune response in the mouth. This combination makes it harder for gums to heal and fight off infection. untreated gum disease acts as a source of inflammation for the entire body.
Stubborn Belly Fat
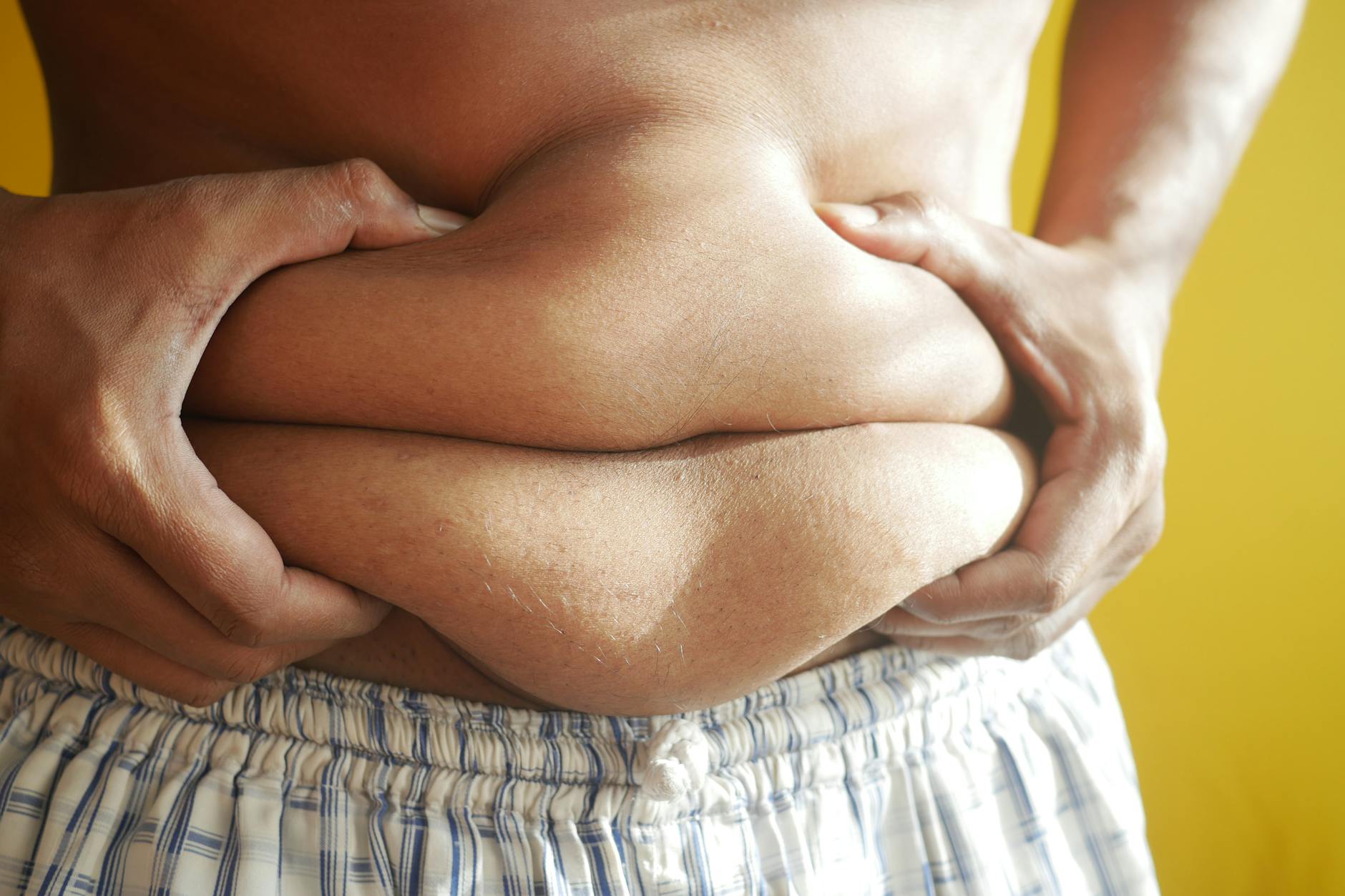
Fructose causes the liver to accumulate fat which is often stored in the abdominal area. This visceral fat wraps around organs and poses significant health risks. It is metabolically active and releases inflammatory substances into the body. shedding this specific type of fat usually requires a significant reduction in fructose intake.
Darkening Skin Folds

High insulin levels can cause skin cells to reproduce too rapidly. This results in patches of skin turning dark and velvety in texture. These patches often appear in the neck or armpits and groin areas. This condition serves as a visible marker of insulin resistance in the body.
Temporary Blurred Vision

High levels of blood sugar can pull fluid from the lenses of the eyes. This changes the shape of the lens and affects the ability to focus properly. Vision may become blurry until blood sugar levels stabilize again. Long-term exposure to high glucose can cause permanent damage to the blood vessels in the eyes.
Slow Wound Healing
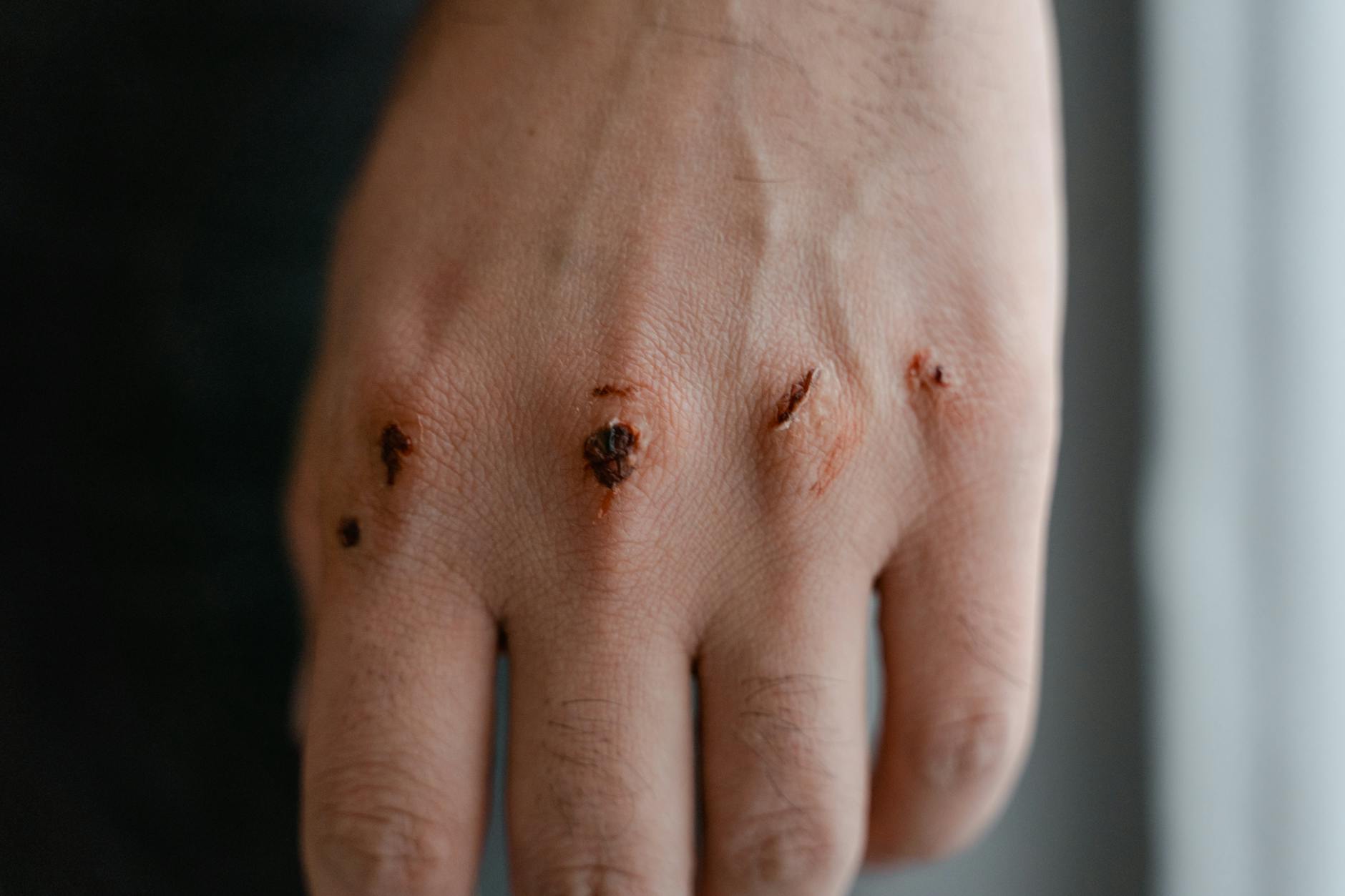
Excess sugar stiffens blood vessels and reduces circulation throughout the body. Poor blood flow means nutrients and oxygen cannot reach wounds efficiently. This delay impairs the body’s natural healing process for cuts and bruises. Infections are also more likely to occur in wounds when blood sugar is high.
Dulled Taste Buds

Overloading the palate with sweet flavors desensitizes the taste buds over time. You may find that you need increasingly sweeter foods to register the same taste. Natural sweetness in fruit or vegetables begins to taste bland in comparison. retrying these foods after a sugar detox often reveals their true and vibrant flavors.
Hormonal Imbalances

Insulin interacts with other hormones in the body including estrogen and testosterone. Chronically high insulin can disrupt the delicate balance of these regulatory chemicals. This disruption may lead to issues such as irregular cycles or skin problems. managing sugar intake helps support overall hormonal health and stability.
Irregular Bowel Movements
Diets high in sugar are often low in fiber which is essential for digestion. The lack of bulk in the diet can lead to constipation and irregularity. Alternatively some people experience loose stools due to sugar malabsorption. increasing fiber while reducing sugar promotes a healthier and more predictable digestive tract.
Midday Energy Crashes

Reliance on sugar provides a quick burst of energy followed by a slump. This pattern often leads to a desperate need for a nap in the early afternoon. The body struggles to maintain consistent energy output without complex carbohydrates or fats. balanced meals prevent these debilitating drops in productivity.
Memory and Concentration Issues
High sugar intake can impair the connection between brain cells. This interference affects the ability to learn and retain new information. Chronic inflammation in the brain contributes to these cognitive deficits. fueling the brain with healthy fats and proteins supports better memory function.
Muscle Aches

Systemic inflammation from sugar can manifest as generalized muscle soreness. This pain is not related to exercise but rather to chemical imbalances. The body remains in a state of low-grade stress that prevents muscles from recovering. eliminating inflammatory foods often resolves these unexplained aches.
Would you like to hear about similar signs related to salt intake or hydration levels in the comments?




