Modern smartphones are incredible tools but their utility is strictly limited by the lifespan of their internal lithium-ion batteries. Users often blame the hardware or the manufacturer when daily habits and settings are actually the primary culprits for rapid power depletion. Making small adjustments to how a device operates can result in hours of extra usage time without compromising essential functionality. Understanding exactly which behaviors consume the most energy empowers users to take control of their digital experience. This guide identifies common practices that silently consume power and offers insight into why they are so demanding on your device.
Keeping Screen Brightness at Maximum
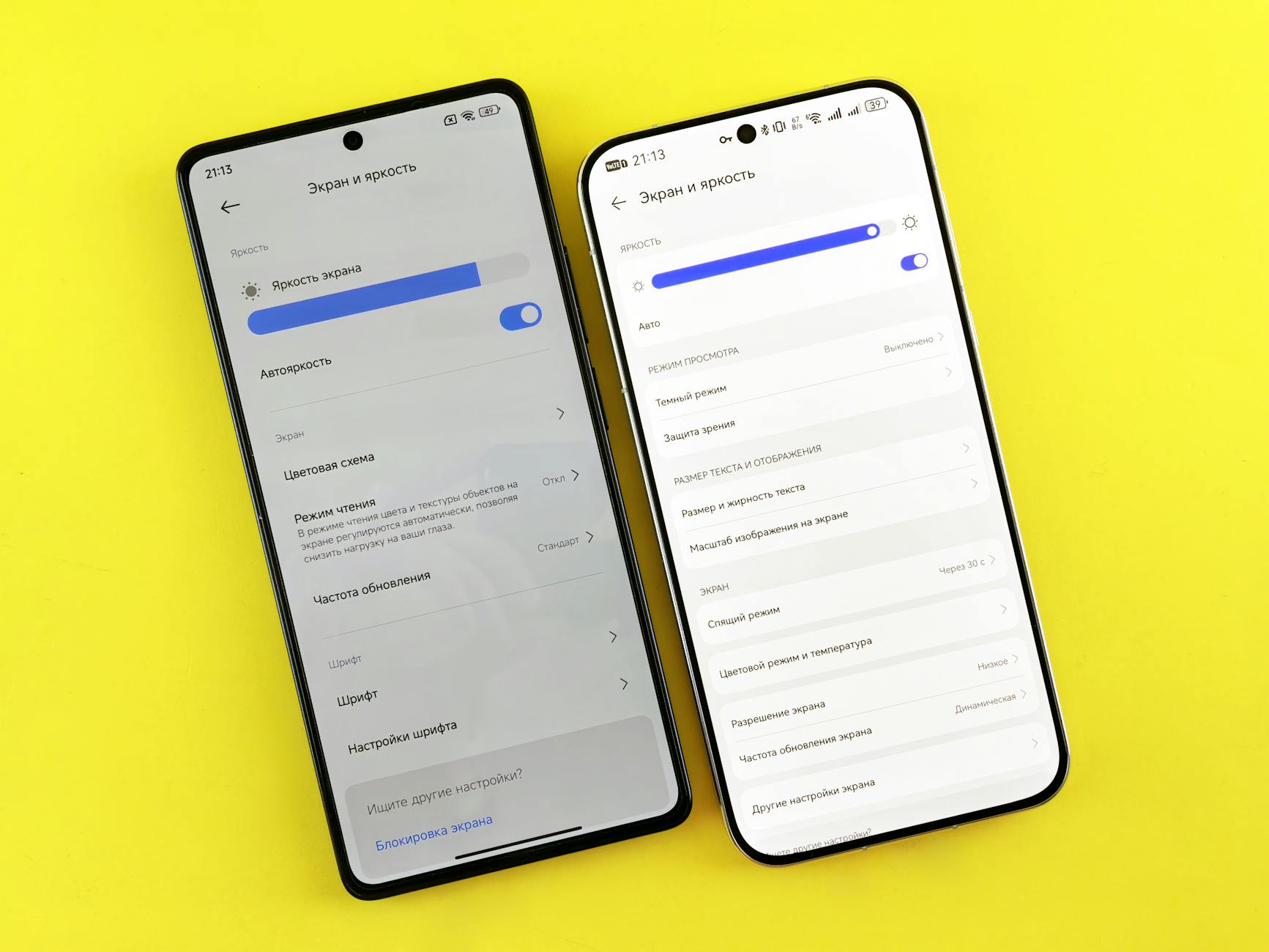
Displaying vivid colors and high brightness levels consumes a significant amount of energy on modern smartphones. Many users leave their screens on full brightness regardless of the ambient lighting conditions around them. Auto-brightness sensors can help regulate this but manual adjustment is often more effective for saving power. Lowering the brightness slider to the lowest comfortable level instantly reduces the power draw from the display panel. This simple habit preserves battery life significantly over the course of a long day.
Using Vibration for All Notifications
The small motor inside a phone that creates physical vibrations requires much more energy than generating a simple sound. Users who keep their phones on vibrate for every text and email alert are constantly activating this mechanical component. The power draw becomes substantial when a device receives dozens of notifications throughout the day. Silent mode without vibration or a low-volume ringtone offers a much more energy-efficient alternative. Reserving haptic feedback only for calls ensures that the battery is not wasted on trivial alerts.
Leaving Location Services On for Every App

GPS tracking is one of the most power-hungry features available on any mobile device. Many applications request access to location data even when it is not essential for their core function. Keeping these permissions active means the phone is constantly communicating with satellites and cell towers to pinpoint coordinates. Auditing app permissions restricts location access to only when the app is actually in use. This prevents background mapping processes from draining the battery while the phone sits in a pocket.
Forcing Apps to Close Manually

People often swipe away all open applications in the belief that an empty multitasking view saves battery power. Modern operating systems are designed to freeze background apps efficiently so they do not consume resources while idle. Force closing an app removes it from RAM and requires the processor to work harder when reloading it later. This cycle of closing and reopening actually uses more energy than simply letting the operating system manage background tasks. Trusting the automated memory management of the device is generally the better approach for longevity.
Ignoring Dark Mode on OLED Screens

Smartphones with OLED displays light up each individual pixel separately to create images on the screen. Using a bright or white background requires every pixel to be illuminated and consume power simultaneously. Dark mode or black wallpapers allow the device to turn off pixels entirely in black areas. This technology saves a measurable amount of energy whenever the screen is active. Switching the system interface to a darker theme utilizes the hardware efficiency of OLED panels to their full potential.
Keeping Wi-Fi Scanning Active

Phones constantly search for available Wi-Fi networks to improve location accuracy and connection speed. This scanning process continues in the background even when Wi-Fi is toggled off in the control center. The radio remains active as it pings for nearby routers and access points while you move through the city. Turning off Wi-Fi scanning deep within the location settings stops this invisible searching behavior. Disabling the feature prevents the battery from working to find networks you have no intention of joining.
Using Dynamic or Live Wallpapers

Animated backgrounds look visually appealing but require constant processing power to render the movement. The graphics processing unit must stay active whenever the home screen or lock screen is visible to the user. This persistent activity prevents the phone from operating in its most efficient low-power state. Static images require zero additional processing once they are loaded into memory. Choosing a still photo over a moving animation is an easy way to reduce the load on the graphics processor.
Enabling Push Notifications for Everything

Every notification that lights up the screen wakes the device from its low-power sleep mode. Social media apps and games often send frequent alerts that provide little value but consume real power. The screen activates and the radio receives data each time a new like or comment occurs. Curating the notification list to include only essential communication apps keeps the phone asleep for longer periods. Reducing the frequency of wake-ups drastically improves the standby time of the battery.
Allowing Background App Refresh

Apps often update their content silently so that new information is ready the moment they are opened. This convenience feature means that data is being downloaded and processed even when the phone appears idle. Social media feeds and news apps are particularly aggressive with this background activity. Turning off background refresh for non-critical apps ensures they only use power when you actively choose to launch them. This setting change stops the device from working overtime on tasks you are not currently watching.
Leaving Bluetooth On When Idle

Bluetooth radios have become more efficient but they still consume power when searching for connections. Keeping the connection active without any paired devices creates a constant low-level drain on the system. The phone continuously broadcasts a signal looking for headphones or speakers that may not be nearby. Toggling Bluetooth off when not using accessories stops this unnecessary searching process entirely. It ensures that the radio is only drawing power when a connection is actually required.
Setting a Long Auto-Lock Timeout

The display is the biggest battery drain and keeping it on when you are not looking at it wastes energy. Many users set their screen timeout to five minutes or never to avoid unlocking the device frequently. This habit means the screen remains fully lit for minutes after the phone is set down on a table. Reducing the auto-lock time to thirty seconds ensures the display powers down almost immediately after use. This small adjustment accumulates significant savings throughout a day of frequent phone interaction.
Streaming High-Definition Video on Cellular Data

Streaming video requires the screen to be on while the modem downloads heavy amounts of data continuously. Doing this over a cellular network forces the radio to work much harder than it would on a stable Wi-Fi connection. The combination of high data throughput and display usage creates a massive power demand. Downloading content ahead of time over Wi-Fi eliminates the need for real-time cellular data transfer. Watching saved videos offline is a far more efficient way to consume media on the go.
Using Voice Assistants with Always-Listening Mode

Voice assistants offer hands-free convenience by waiting for a specific wake word to activate. This feature requires the microphone to be powered on and the processor to analyze audio input constantly. The device never truly rests because it must remain alert for the command phrase at all times. Disabling the “Hey Google” or “Hey Siri” detection removes this persistent background processing task. Triggering the assistant manually with a button press conserves the energy used by constant audio monitoring.
Staying in Areas with Poor Signal Strength

A phone struggles to maintain a connection when the cellular signal is weak or obstructed. The internal antenna creates a powerful signal boost to try and reach the nearest cell tower. This amplification process generates heat and drains the battery rapidly as the phone fights to stay online. Switching to airplane mode in areas with known poor reception stops this futile power usage. Reconnecting only when you are in a range of a strong signal saves the battery from exhaustion.
Keeping Haptic Feedback on the Keyboard

Keyboard vibration provides physical confirmation that a key press has been registered by the software. This feature activates the vibration motor hundreds of times during a single text conversation or email draft. The cumulative effect of typing out long messages with haptics enabled is a significant drain on power. Disabling keyboard vibration relies on visual or audio cues instead of mechanical movement. Removing this motor activity for every character typed preserves battery life for more important functions.
Using 5G When 4G Is Sufficient

The latest 5G networks offer incredible speeds but the modems required to access them are power-intensive. Phones often switch between 5G and 4G rapidly if the coverage in a specific area is spotty. This constant switching and the higher power requirements of 5G antennas deplete the battery faster than LTE connections. Forcing the phone to use 4G LTE can result in better battery performance for general browsing and messaging. Users rarely notice the speed difference for basic tasks while the battery benefits are substantial.
Enabling Automatic App Updates
App stores often download and install updates in the background as soon as they become available. This process involves downloading large files and installing software while the user is unaware. The processor and Wi-Fi radio work simultaneously to complete these tasks without permission. Scheduling updates to occur only when the phone is charging prevents this drain during the day. Manual updating allows the user to choose a convenient time that does not impact battery life.
Keeping Widgets on the Home Screen
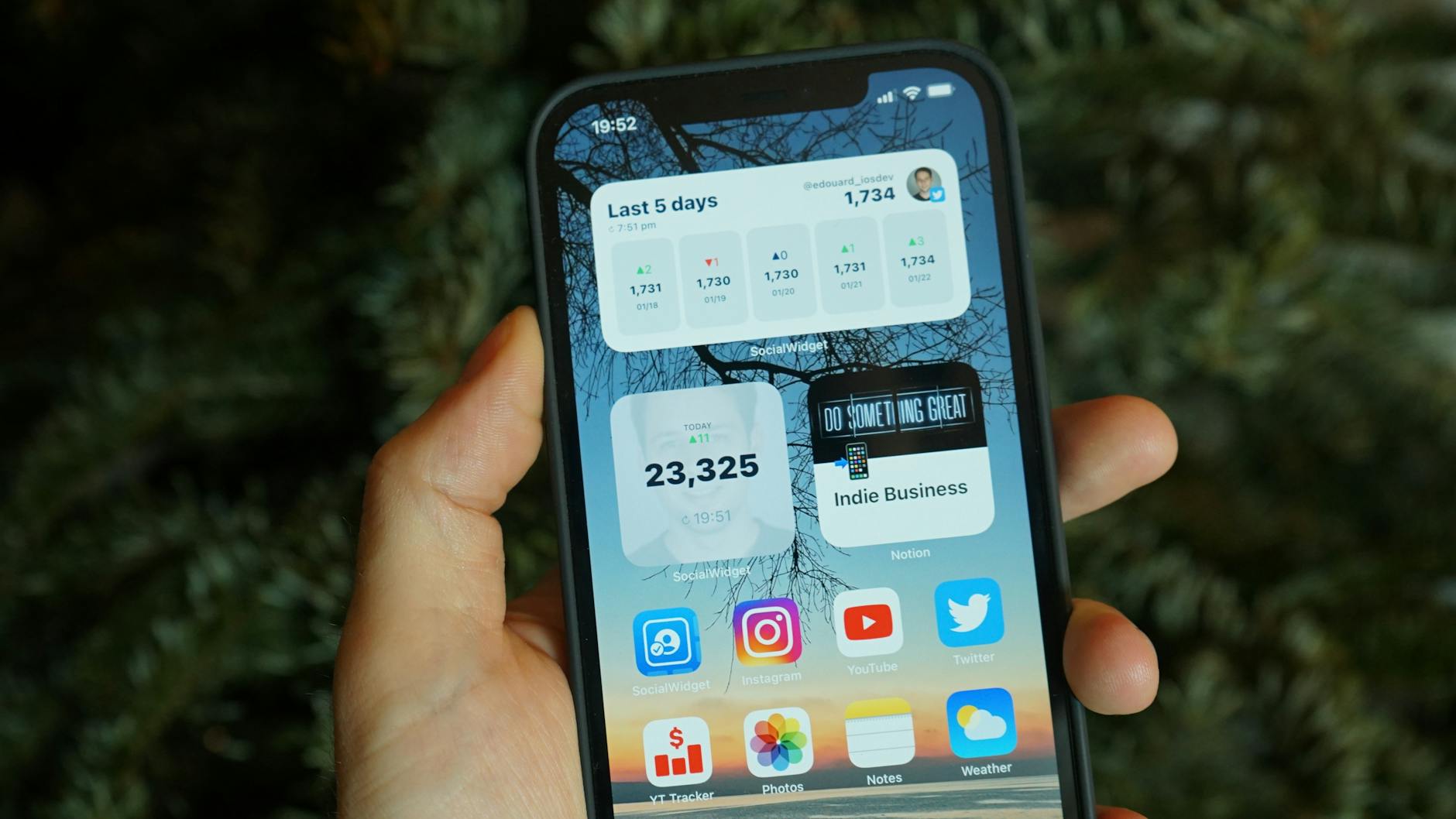
Widgets provide at-a-glance information like weather or stock prices without opening an app. These small programs refresh their data frequently to ensure the information displayed is current. Having multiple widgets on the home screen means multiple background processes are running constantly. Removing non-essential widgets reduces the number of data requests the phone makes silently. A cleaner home screen often correlates directly with better battery performance.
Ignoring Software Updates
Operating system updates often include optimizations that improve how the phone manages power and resources. Ignoring these updates can leave the device running inefficient code or buggy processes. Developers release patches specifically to fix battery drain issues discovered in previous versions. Keeping the software current ensures the phone benefits from the latest power management protocols. Running an outdated operating system often means missing out on critical efficiency improvements.
Exposure to Extreme Temperatures

Batteries rely on chemical reactions that are sensitive to both extreme heat and extreme cold. Leaving a phone in a hot car or using it in freezing weather degrades the battery’s ability to hold a charge. The internal management system works overtime to regulate safety which consumes additional energy. Keeping the device at room temperature allows the chemical processes to function optimally. Physical protection from the elements is just as important as software settings for battery health.
Using High Refresh Rates Unnecessarily
Modern flagship phones feature screens that refresh up to 120 times per second for smoother scrolling. This high refresh rate demands more power from the graphics processor and the display panel. Many devices allow users to cap the refresh rate at the standard 60Hz to save energy. Limiting this feature is often unnoticeable during video watching or reading text. Disabling high refresh rates is a trade-off that yields considerable gains in daily battery longevity.
Leaving Near Field Communication On

Near Field Communication or NFC is primarily used for contactless payments and quick pairing. Keeping the NFC chip active means it is constantly ready to interact with payment terminals or tags. While the power draw is low it is still a completely unnecessary drain when not in a store. Adding an NFC toggle to the control center makes it easy to turn on only when needed. Turning it off prevents the chip from idling in a standby state all day.
Using Bright Wallpapers

The choice of wallpaper affects battery life even on non-OLED screens by influencing brightness perception. A very bright and colorful image often compels the user to increase the screen brightness to see icons clearly. Subtle and darker wallpapers provide better contrast and allow for lower backlight settings. This indirect effect on user behavior helps maintain lower energy consumption. Choosing a muted background image is a passive way to encourage power-saving habits.
Enabling Automatic Downloads in Messaging Apps

Messaging platforms like WhatsApp or Telegram often download every photo and video received automatically. This activity uses data and writes files to storage every time a media message arrives. Group chats can generate hundreds of megabytes of downloads that the user may never even look at. Disabling auto-download means media is only retrieved when you tap on it. This setting prevents the radio and storage controller from working on unwanted content.
Constant Fitness Tracking

Fitness apps often use the accelerometer and gyroscope to track steps and movement throughout the day. Having multiple apps tracking the same physical activity creates redundant background processing. The phone must wake up sensors and record data for each individual application. Centralizing health data into one app and disabling tracking permissions for others reduces sensor usage. Consolidating these measurements ensures that physical activity is tracked efficiently.
Please share which of these habits you intend to change in the comments.





