Consuming excess sodium often goes unnoticed until physical symptoms begin to manifest throughout the body. Many common dietary choices rely heavily on hidden salts for preservation and flavor enhancement. Paying close attention to subtle physical changes can reveal important information about overall sodium intake. Recognizing these warning signals early allows for timely dietary adjustments to protect long term health and well being.
Persistent Thirst

An unquenchable desire for water often indicates a significant imbalance in bodily sodium levels. High salt intake forces the body to draw moisture from cells to dilute the excess sodium in the bloodstream. This cellular dehydration triggers strong signals to the brain demanding immediate fluid replenishment. Constant water consumption without feeling satisfied serves as a clear warning of excessive dietary salt.
Frequent Urination

Kidneys must work overtime to process and eliminate high amounts of dietary sodium from the system. This increased filtration process naturally leads to a much higher volume of urine production throughout the day and night. Frequent trips to the bathroom disrupt daily activities and severely impact sleep quality. This constant fluid processing acts as a direct mechanical response to elevated salt consumption.
Mild Swelling
Excess sodium directly causes the body to retain extra water within its tissues. This fluid accumulation often appears as noticeable puffiness in the face and extremities. Rings may suddenly feel tight on fingers while shoes become uncomfortably snug around the ankles. This physical expansion directly reflects the cellular struggle to balance high sodium concentrations.
Elevated Blood Pressure
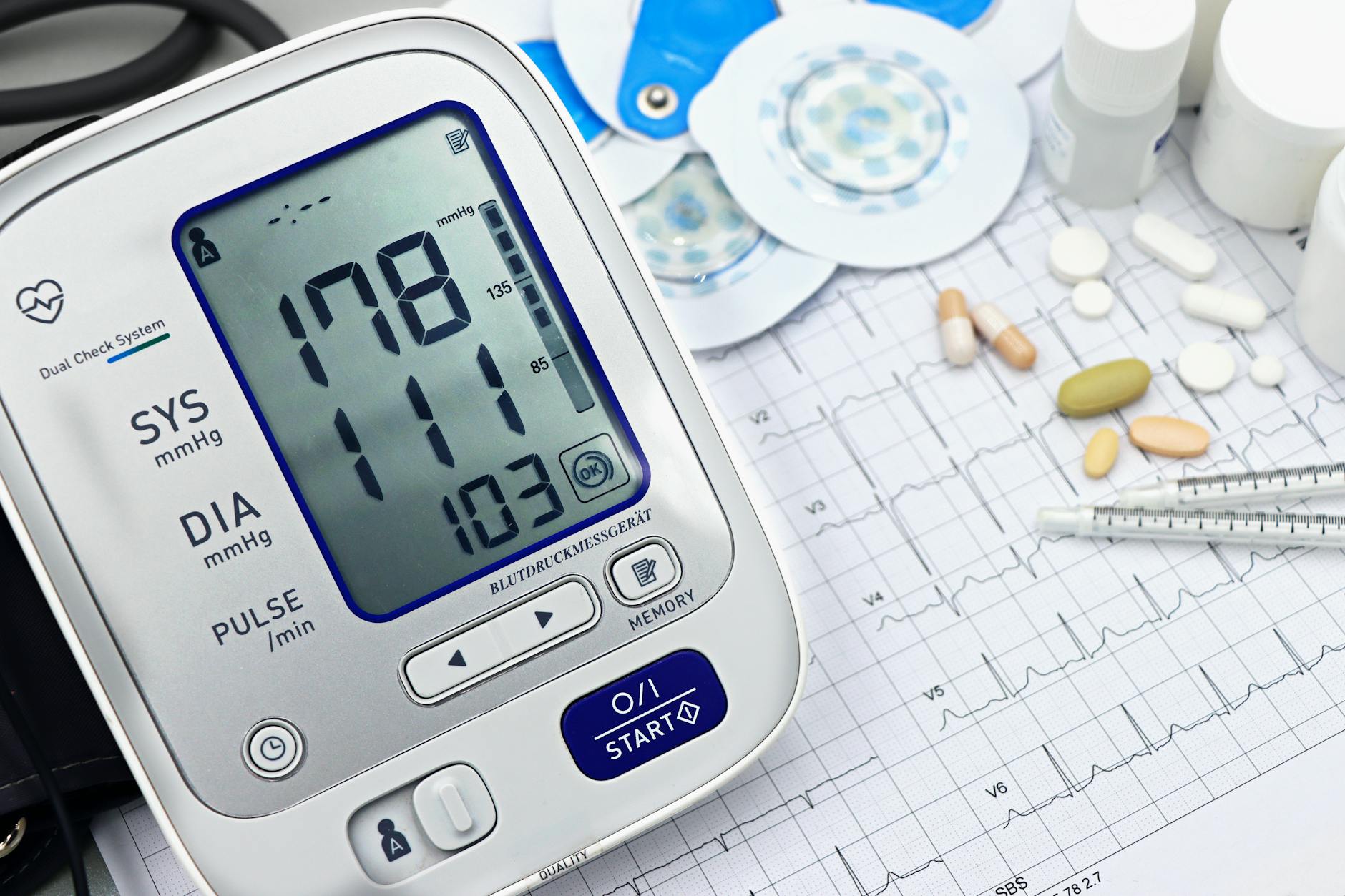
Sodium pulls extra water into the bloodstream and significantly increases the overall volume of circulating blood. This expanded fluid volume places intense outward pressure against the delicate walls of blood vessels. Healthcare providers frequently identify this specific metric as a primary indicator of excessive dietary salt. Consistently high readings require immediate attention to prevent severe cardiovascular complications over time.
Frequent Headaches

Sudden expansion of blood vessels triggered by excess sodium creates painful pressure in the head. These dull throbbing sensations often occur shortly after consuming meals heavily laden with hidden salts. The resulting dehydration further exacerbates this cranial discomfort and reduces overall cognitive focus. Monitoring the timing of head pain often reveals a direct correlation with salty food consumption.
Salt Cravings

A diet consistently high in sodium actually alters the sensitivity of taste buds over time. Foods with normal salt levels begin to taste incredibly bland and unappealing. This sensory adaptation creates a vicious cycle where individuals continuously seek out increasingly salty snacks. Breaking this flavor dependency requires a conscious period of taste bud recalibration through low sodium choices.
Dry Mouth

The physical sensation of a parched mouth stems directly from sodium stripping moisture from mucous membranes. Lips may become chapped while the tongue feels uncomfortably dry and slightly swollen. Saliva production drops significantly as the body attempts to conserve vital fluids for internal dilution. This uncomfortable dryness persists until sodium levels return to a balanced state.
Poor Sleep Quality

Consuming salty meals late in the evening severely disrupts natural circadian rhythms and rest cycles. The resulting physical discomfort and frequent urges to urinate prevent the achievement of deep restorative sleep. Individuals often wake up feeling groggy and physically exhausted despite spending adequate hours in bed. Restricting salt intake during the afternoon greatly improves overall nocturnal recovery.
Weight Fluctuations

The bathroom scale often displays rapid and confusing increases over incredibly short periods. This sudden weight gain primarily represents trapped water rather than actual body fat accumulation. A single high sodium meal can easily cause the body to hold several pounds of excess fluid. Tracking these rapid changes helps identify specific dietary triggers causing unwanted water retention.
Digestive Discomfort

High sodium concentrations directly irritate the sensitive lining of the stomach and intestinal tract. This chemical irritation frequently manifests as mild nausea and persistent abdominal cramping after meals. The disruption of natural fluid balance in the gut also contributes to irregular bowel movements. Choosing fresh foods over processed alternatives dramatically reduces this gastrointestinal distress.
Kidney Stones
Excessive dietary salt increases the amount of calcium that kidneys must actively filter into the urine. This elevated calcium concentration creates the perfect environment for painful mineral crystals to form. These solid masses cause excruciating pain as they travel through the delicate urinary tract system. Reducing sodium intake remains a critical preventative measure against these debilitating formations.
Cognitive Fog

Dehydration caused by sodium imbalances severely impacts optimal brain function and mental clarity. Individuals frequently report an inability to concentrate on complex tasks or recall simple daily details. This mental sluggishness typically clears up once proper hydration and electrolyte balances are fully restored. Maintaining moderate salt intake ensures the brain receives adequate fluid support for peak performance.
Muscle Cramps

Proper muscle function relies on a delicate balance of various essential electrolytes including sodium and potassium. An overwhelming influx of salt disrupts this crucial chemical equilibrium within muscle fibers. This imbalance triggers sudden and painful involuntary contractions often occurring during rest. Restoring proper mineral ratios through dietary adjustments quickly resolves these uncomfortable muscular spasms.
Weakened Bones
The body naturally leaches calcium from skeletal structures to help process incredibly high sodium loads. This continuous mineral depletion gradually weakens overall bone density and structural integrity over time. Weakened bones become highly susceptible to unexpected fractures and long term degenerative conditions. Preserving skeletal health requires careful monitoring of daily salt consumption from all food sources.
Puffy Eyes

The delicate skin surrounding the eyes easily traps excess fluid caused by dietary sodium spikes. Waking up with swollen under eye bags serves as a common visible symptom of late night salty snacks. This facial puffiness usually subsides slowly as the body processes and eliminates the offending minerals. Applying cold compresses offers temporary relief while internal sodium levels gradually stabilize.
Enlarged Heart Muscle
Constantly pumping an increased volume of blood forces the heart muscle to work much harder than intended. This chronic overexertion causes the muscular walls of the heart to thicken and become less efficient. A thickened heart struggles to pump oxygenated blood effectively throughout the entire body. Controlling dietary salt prevents this dangerous structural modification and preserves essential cardiovascular function.
Reduced Exercise Stamina

High sodium levels create systemic dehydration that severely limits physical endurance and athletic performance. Muscles fatigue much faster when deprived of optimal fluid balance during strenuous activities. The cardiovascular system also struggles to deliver necessary oxygen when burdened by excess blood volume. Athletes must carefully balance their salt intake to maintain peak physical capabilities.
Chronic Fatigue

The immense physical strain of processing heavy sodium loads drains vital energy reserves. Organs working overtime to restore internal equilibrium leave the body feeling constantly exhausted and depleted. This deep weariness persists regardless of caffeine intake or extended periods of rest. Lowering salt consumption removes this unnecessary metabolic burden and naturally restores daily energy levels.
Skin Breakouts
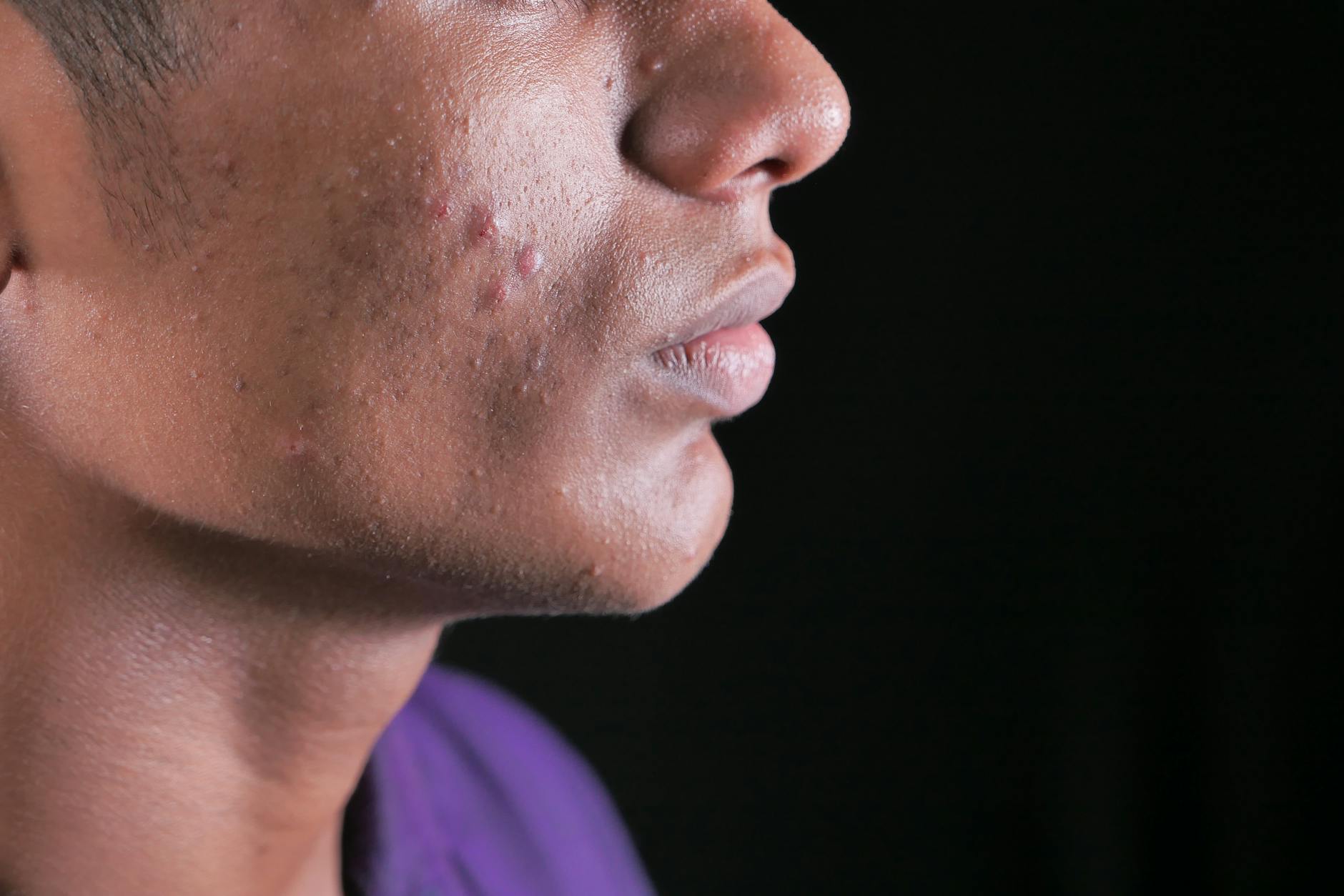
Excessive dietary salt triggers systemic inflammation that often manifests visibly on the skin surface. This internal inflammatory response exacerbates existing acne conditions and promotes new blemishes. Dehydrated skin also overproduces natural oils in a desperate attempt to compensate for lost moisture. Improving dietary habits directly supports a clearer and much healthier facial complexion.
Increased Heart Rate
The circulatory system must rapidly adapt to the increased blood volume caused by water retention. The heart compensates by beating faster to push this heavy fluid load through the vascular network. Individuals may notice their pulse racing even while resting completely comfortably in a chair. This sustained rapid heartbeat indicates a cardiovascular system struggling against high sodium interference.
Please share your personal experiences with managing dietary sodium habits in the comments.





