Coffee is a daily staple for millions of people but consuming it in excess can lead to a variety of uncomfortable physical and mental side effects. Medical professionals warn that exceeding the generally recommended limit of 400 milligrams of caffeine per day often triggers a stress response within the body. Recognizing the subtle and overt signals of overconsumption is crucial for maintaining your long-term wellness and daily balance. The following signs suggest that your current coffee intake might be overwhelming your system.
Persistent Insomnia
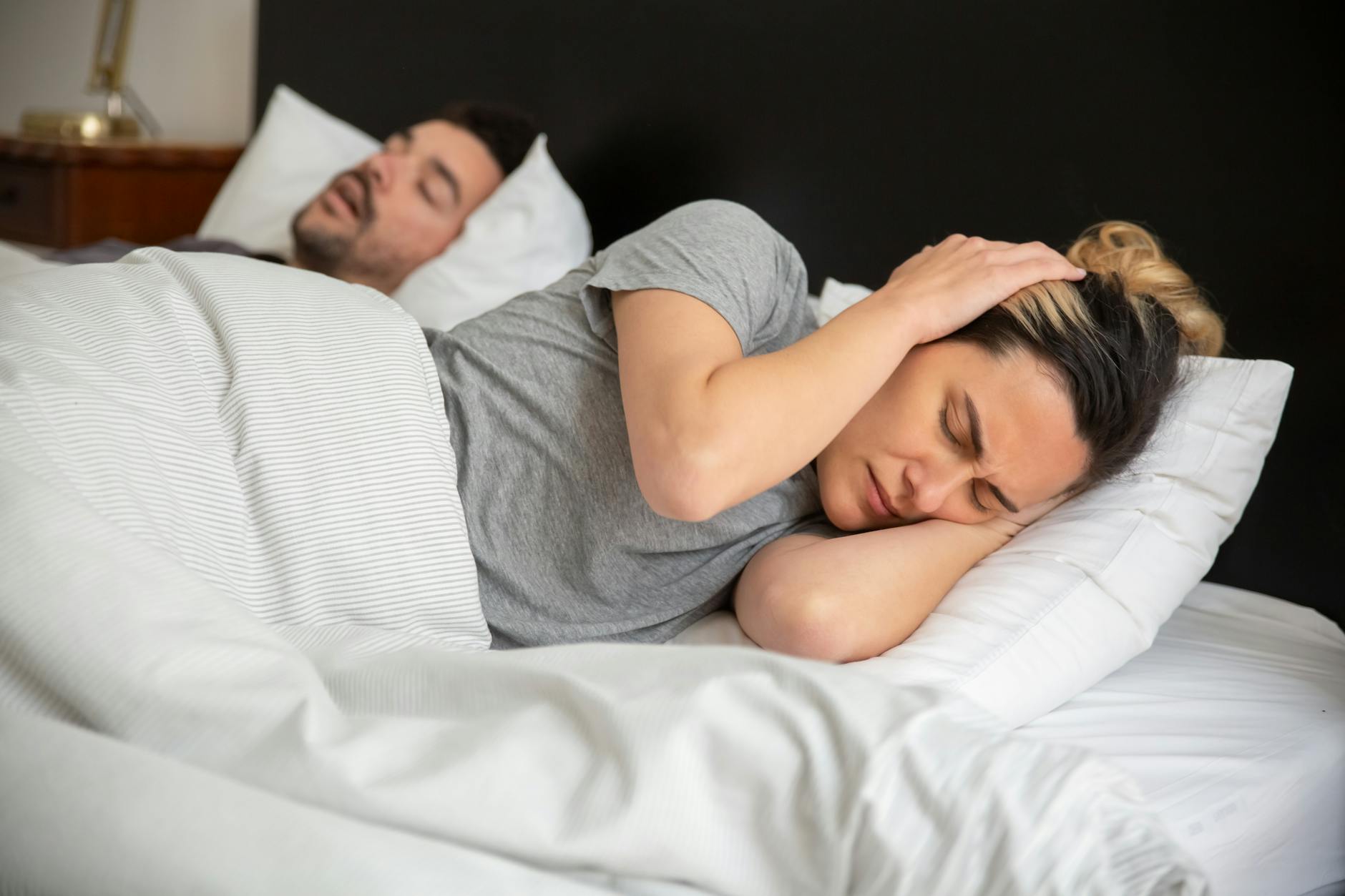

Struggling to fall asleep or staying asleep often indicates that caffeine is lingering in your system too late into the evening. The stimulant works by blocking adenosine receptors in the brain which are responsible for signaling fatigue and helping you drift off. Consuming coffee even six hours before bedtime can significantly disrupt your natural circadian rhythm and reduce deep sleep. This lack of restorative rest often creates a vicious cycle where you feel the need for more caffeine the next day.
Heightened Anxiety
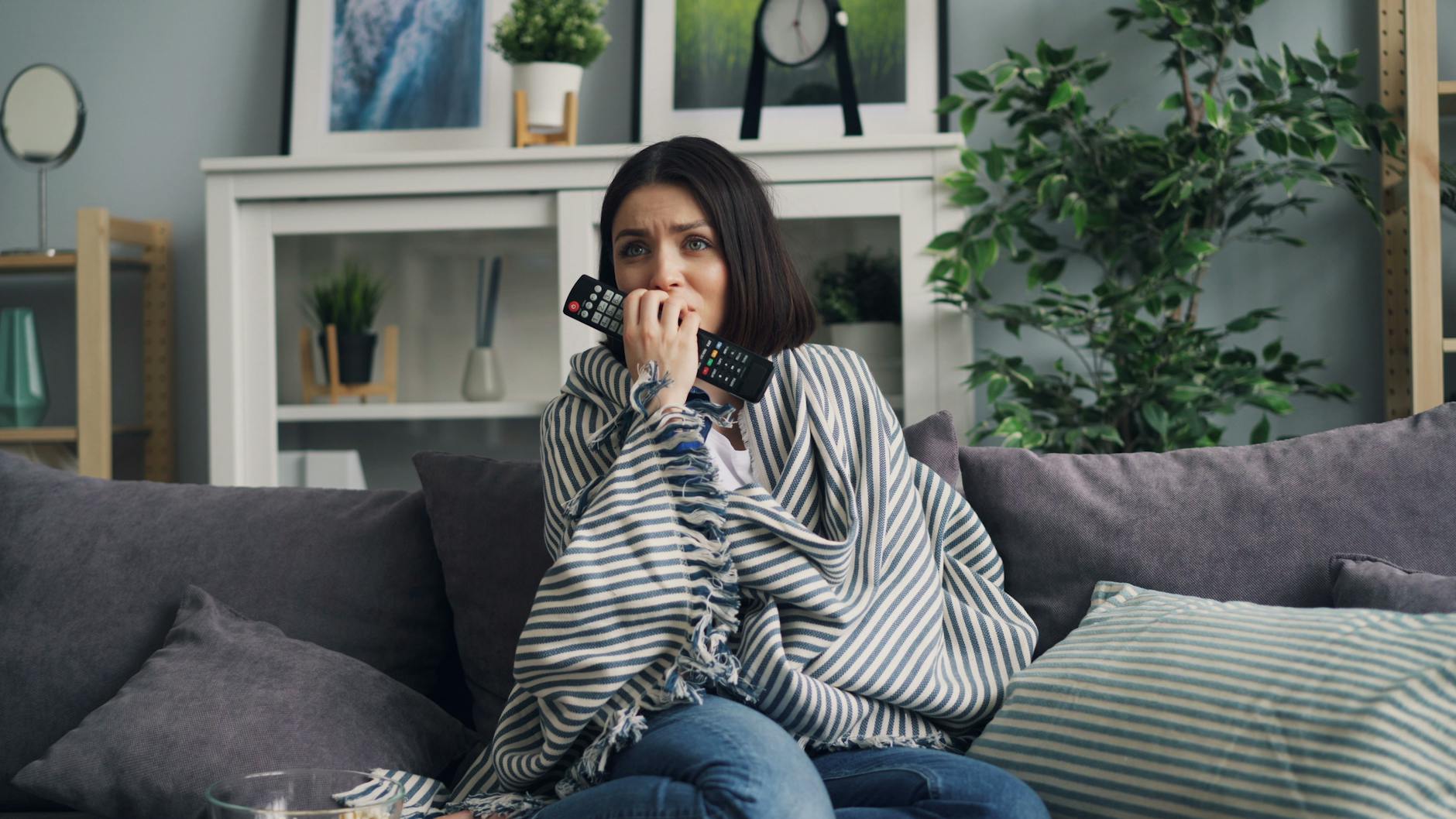

Excessive caffeine consumption stimulates the central nervous system and triggers the release of adrenaline and cortisol. This chemical surge can manifest as feelings of nervousness or an impending sense of doom even when there is no external stressor. You might notice your thoughts racing or an inability to relax despite being in a calm environment. Reducing your intake can often alleviate these unexplained feelings of panic and restore mental equilibrium.
Frequent Headaches

While small amounts of caffeine can sometimes help alleviate head pain it often becomes the cause when consumed in large quantities. Regular overconsumption causes the blood vessels in the brain to constrict and then painfully expand when the caffeine wears off. This effect is commonly known as a rebound headache and creates a dependency on coffee to keep the pain at bay. moderating your intake ensures that your blood vessels remain in a stable state throughout the day.
Digestive Discomfort

Coffee is highly acidic and stimulates the production of stomach acid which can lead to significant gastrointestinal distress. You might experience cramping or general abdominal pain shortly after finishing your cup. The laxative effect of caffeine also accelerates digestion often resulting in loose stools or diarrhea. Switching to low-acid alternatives or limiting consumption can help soothe a sensitive digestive tract.
Heart Palpitations

A feeling of your heart fluttering or beating irregularly is a frightening sign that your caffeine levels are too high. The stimulant effect forces the heart to work harder and beat faster than its normal resting rate. This symptom is particularly common in individuals who are sensitive to stimulants or those who consume energy drinks alongside coffee. It is essential to monitor your heart rate and cut back immediately if you experience these sensations.
Muscle Tremors

You might notice a physical sensation of trembling in your hands or an inability to keep your limbs perfectly still. This physiological response occurs because caffeine excites the motor neurons in your nervous system. The excess energy often manifests as uncontrollable shaking or a general feeling of vibration throughout the body. Reducing your daily dosage helps the nervous system calm down and restores steadiness to your fine motor skills.
Chronic Fatigue
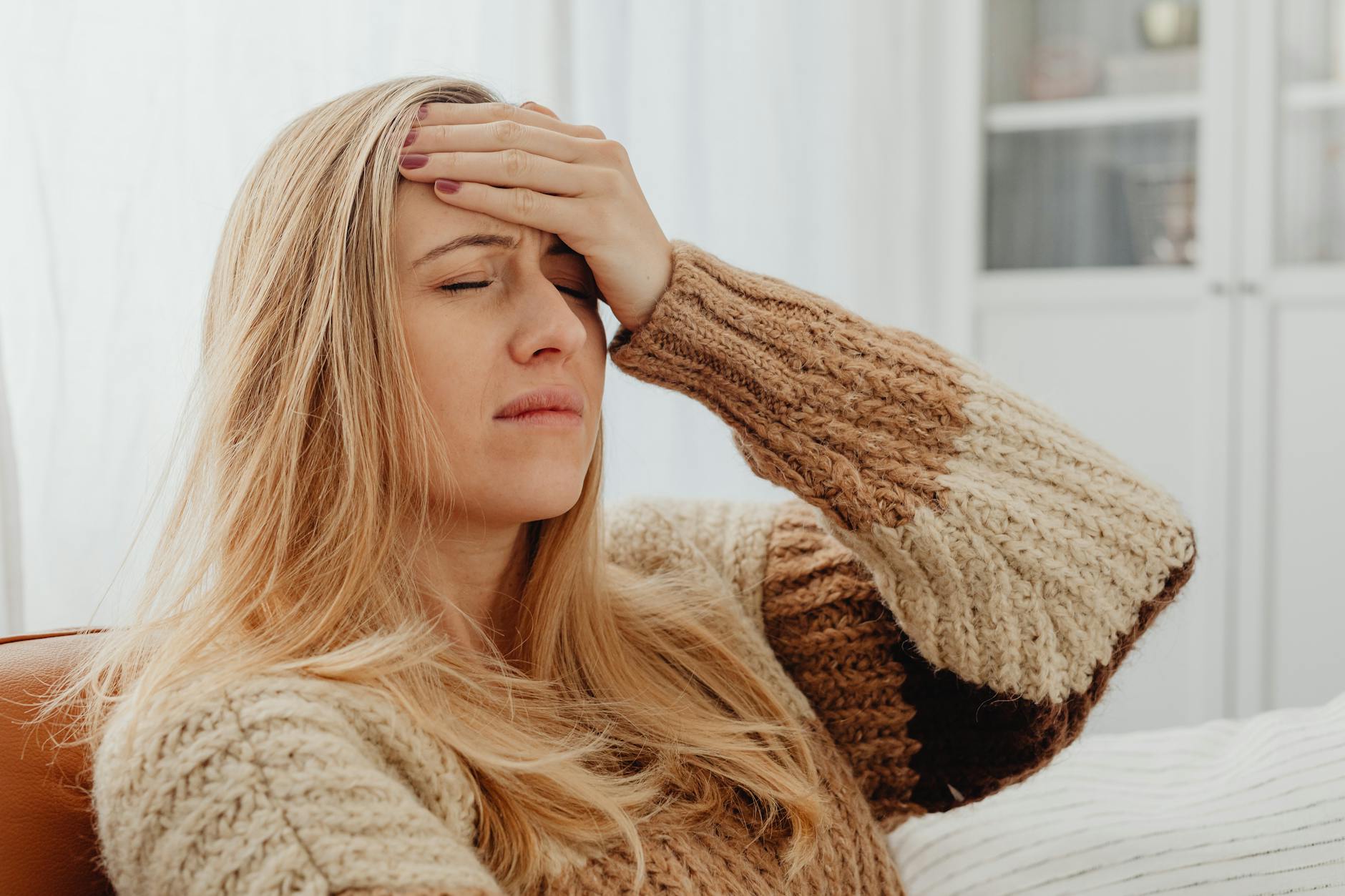

It may seem counterintuitive but drinking too much coffee can actually leave you feeling more tired in the long run. The artificial energy boost eventually wears off and leads to a significant crash that leaves you feeling exhausted. This rebound effect happens because the body builds up adenosine while the caffeine is active and floods the system once it metabolizes. Relying on caffeine for energy masks the body’s true need for rest and recovery.
High Blood Pressure
Caffeine causes a short but dramatic spike in blood pressure levels even if you do not have a history of hypertension. The stimulant blocks a hormone that helps keep your arteries wide and allows blood to flow freely. This temporary increase puts extra strain on your cardiovascular system if it occurs multiple times throughout the day. Doctors often advise those with heart conditions to limit their intake to avoid these potentially dangerous fluctuations.
Irritability
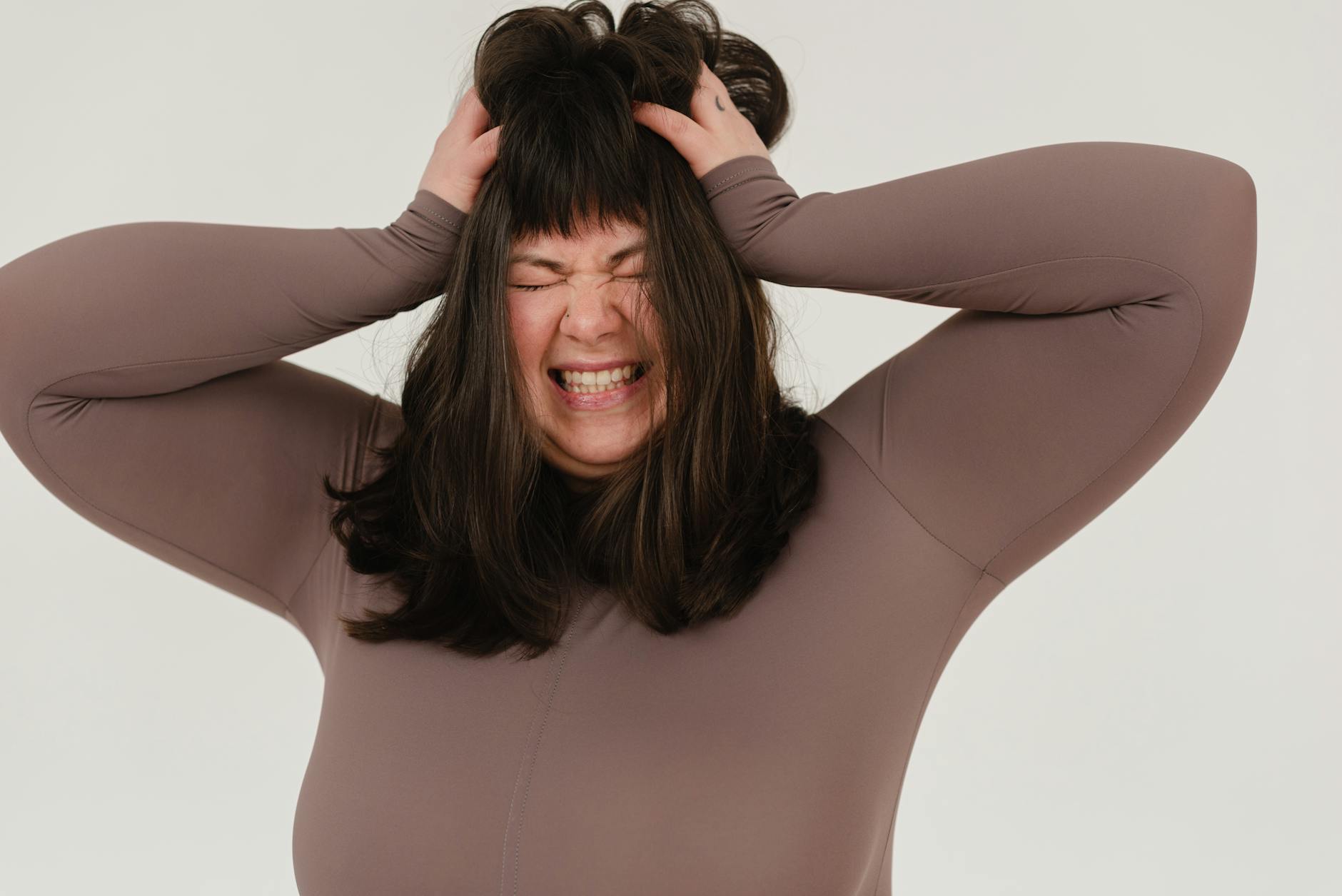

A sudden snap in your temper or feeling easily annoyed by small inconveniences can be a behavioral sign of caffeinism. The overstimulation of the brain’s fight or flight response makes you more reactive to your environment. This agitation is often compounded by the sleep deprivation that accompanies high caffeine intake. Lowering your consumption can help stabilize your mood and improve your interactions with others.
Frequent Urination
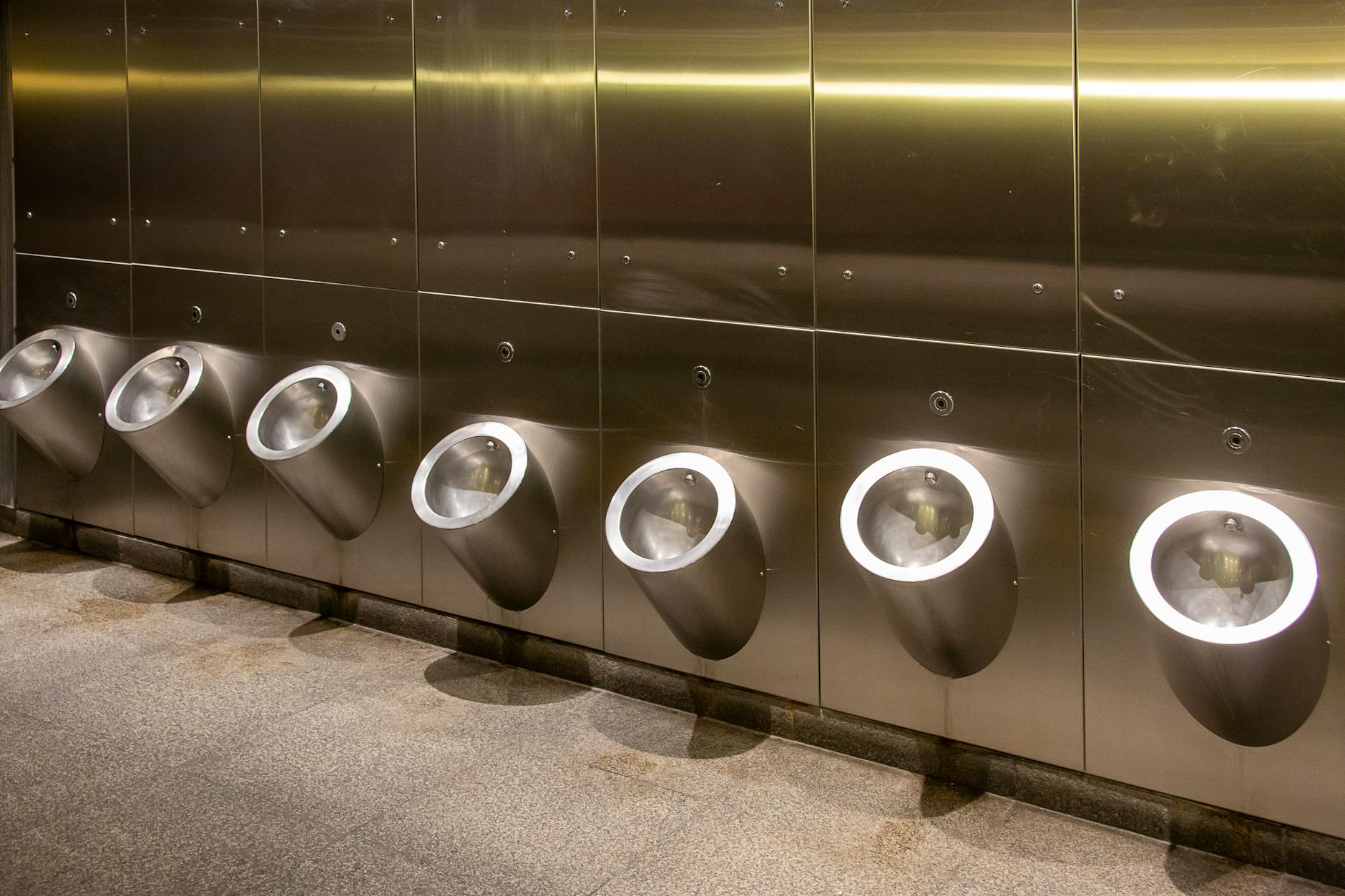

Caffeine acts as a diuretic which means it signals your kidneys to expel more water and salt from the body. You may find yourself needing to use the restroom far more often than is normal for your fluid intake. This increased frequency can lead to dehydration if you are not replenishing your fluids with water. Balancing your coffee habits with ample hydration is key to maintaining proper kidney function.
Dizziness
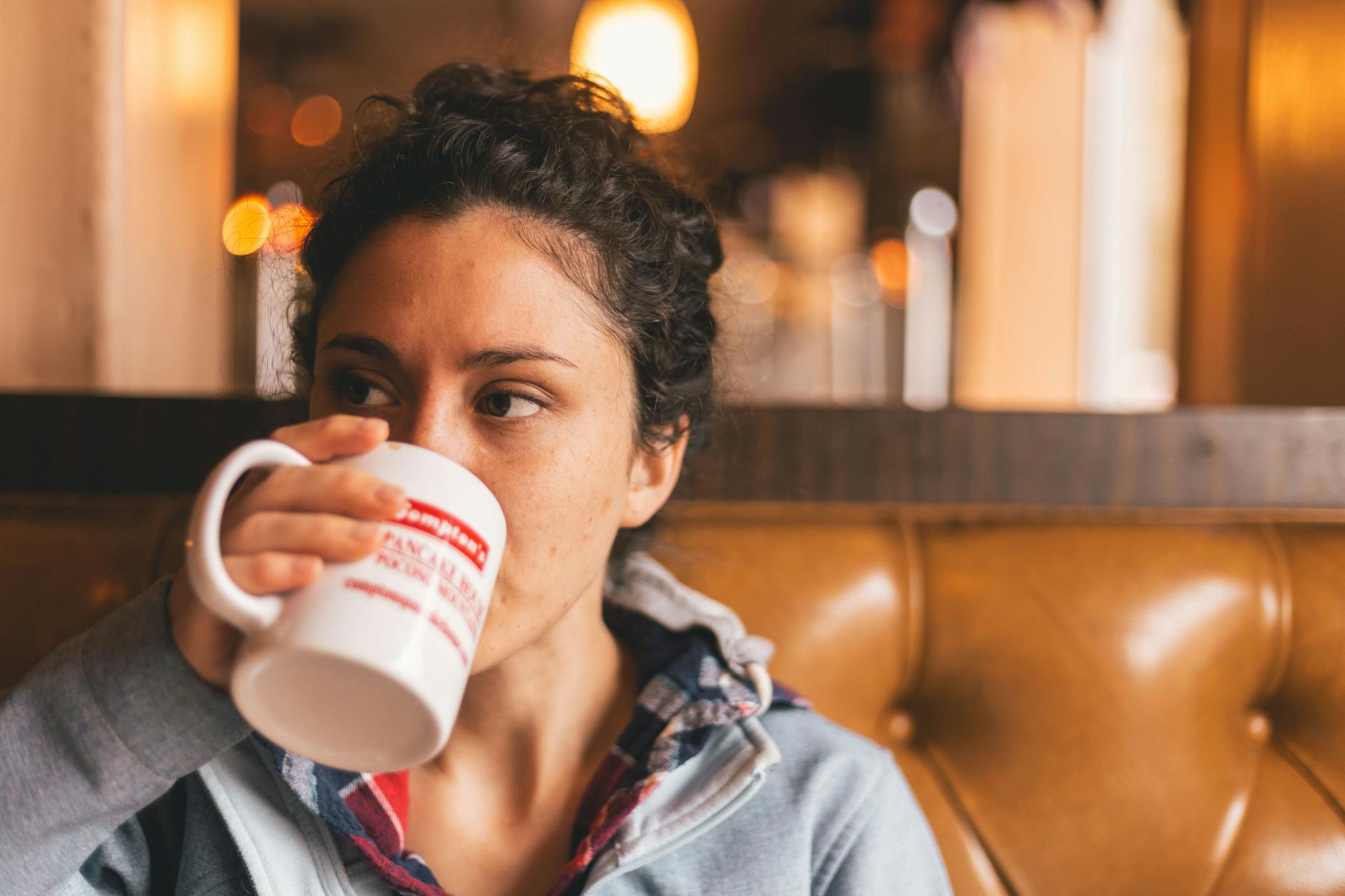

Feeling lightheaded or unsteady on your feet can occur when caffeine restricts blood flow to the brain. This sensation often hits suddenly and can be disorienting or make it difficult to focus on tasks. It serves as a warning sign that your body is struggling to process the amount of stimulant in your bloodstream. Sitting down and drinking water usually helps the feeling pass as the caffeine metabolizes.
Acid Reflux
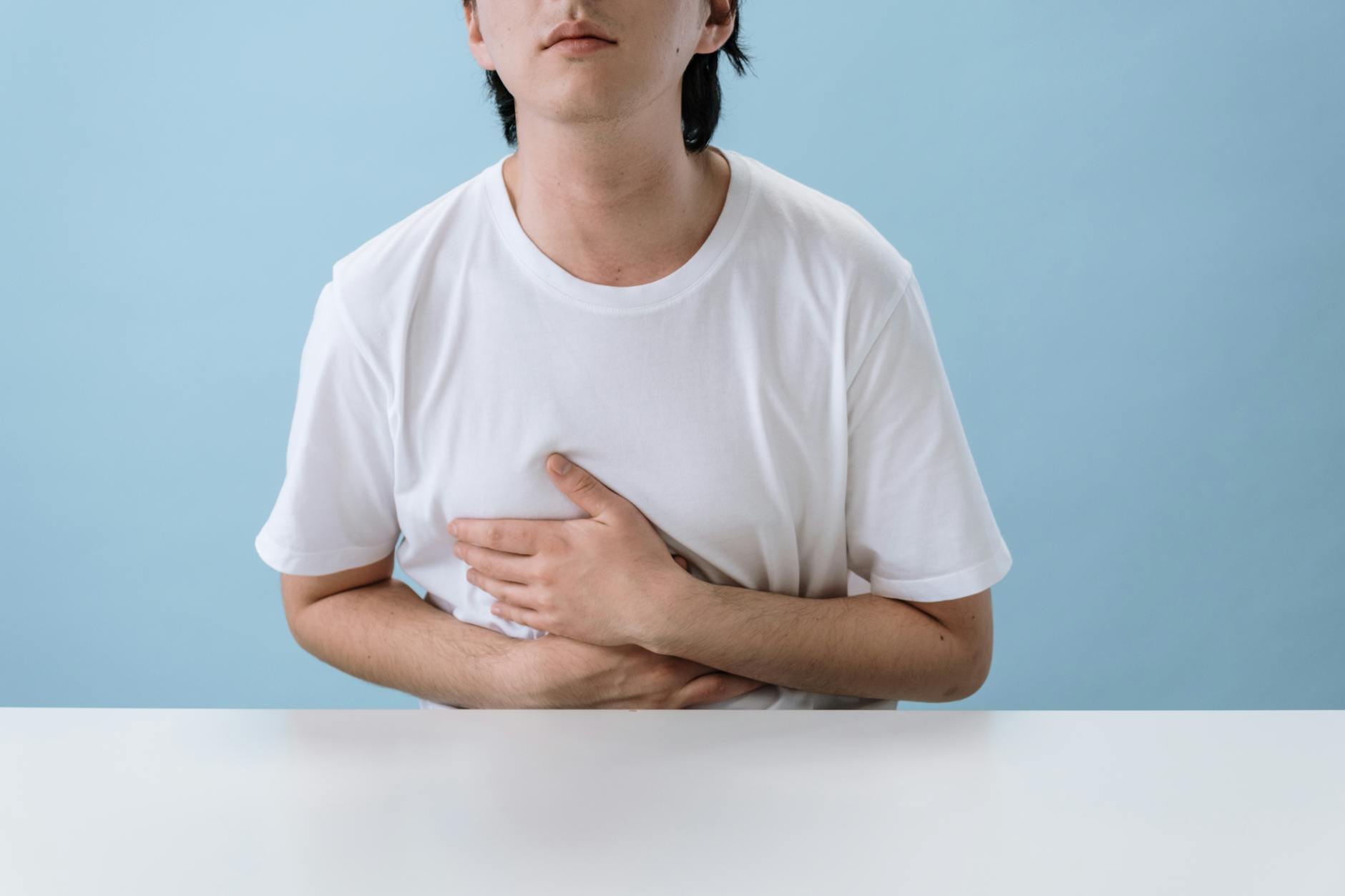

The lower esophageal sphincter muscle relaxes when exposed to large amounts of caffeine and allows stomach acid to travel upward. This process causes a burning sensation in the chest and throat known as heartburn. Chronic exposure can damage the lining of the esophagus and lead to long-term gastrointestinal issues. avoiding coffee on an empty stomach often helps mitigate this uncomfortable burning sensation.
Eyelid Twitching
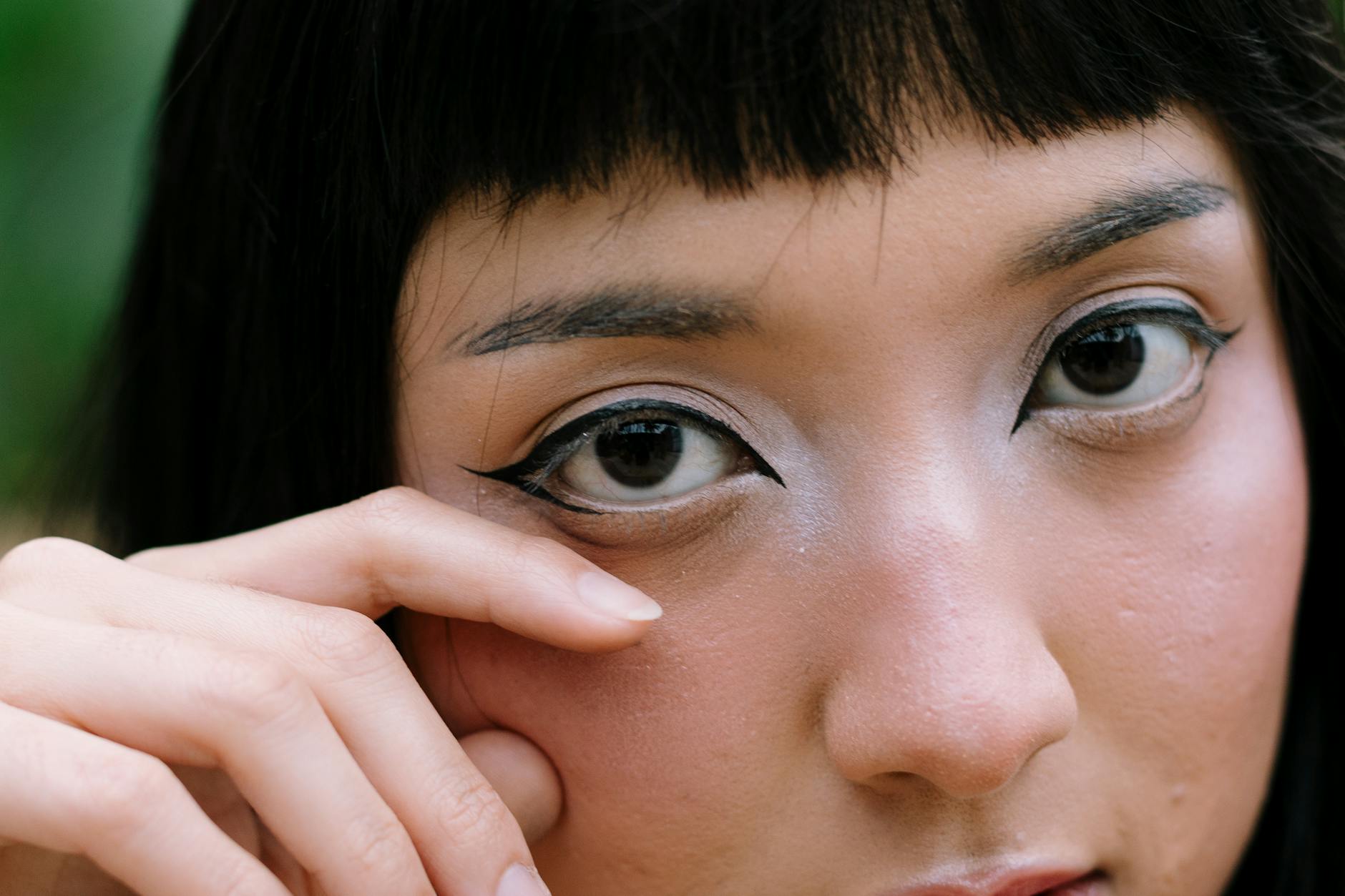

A persistent and involuntary spasm in the eyelid is a classic sign of an overexcited nervous system. Medical experts refer to this condition as myokymia and it is frequently triggered by high stress and high caffeine intake. The twitching is usually harmless but serves as an annoying reminder that your body needs a break from stimulants. Cutting back on your daily cups usually resolves the twitching within a few days.
Rapid Breathing
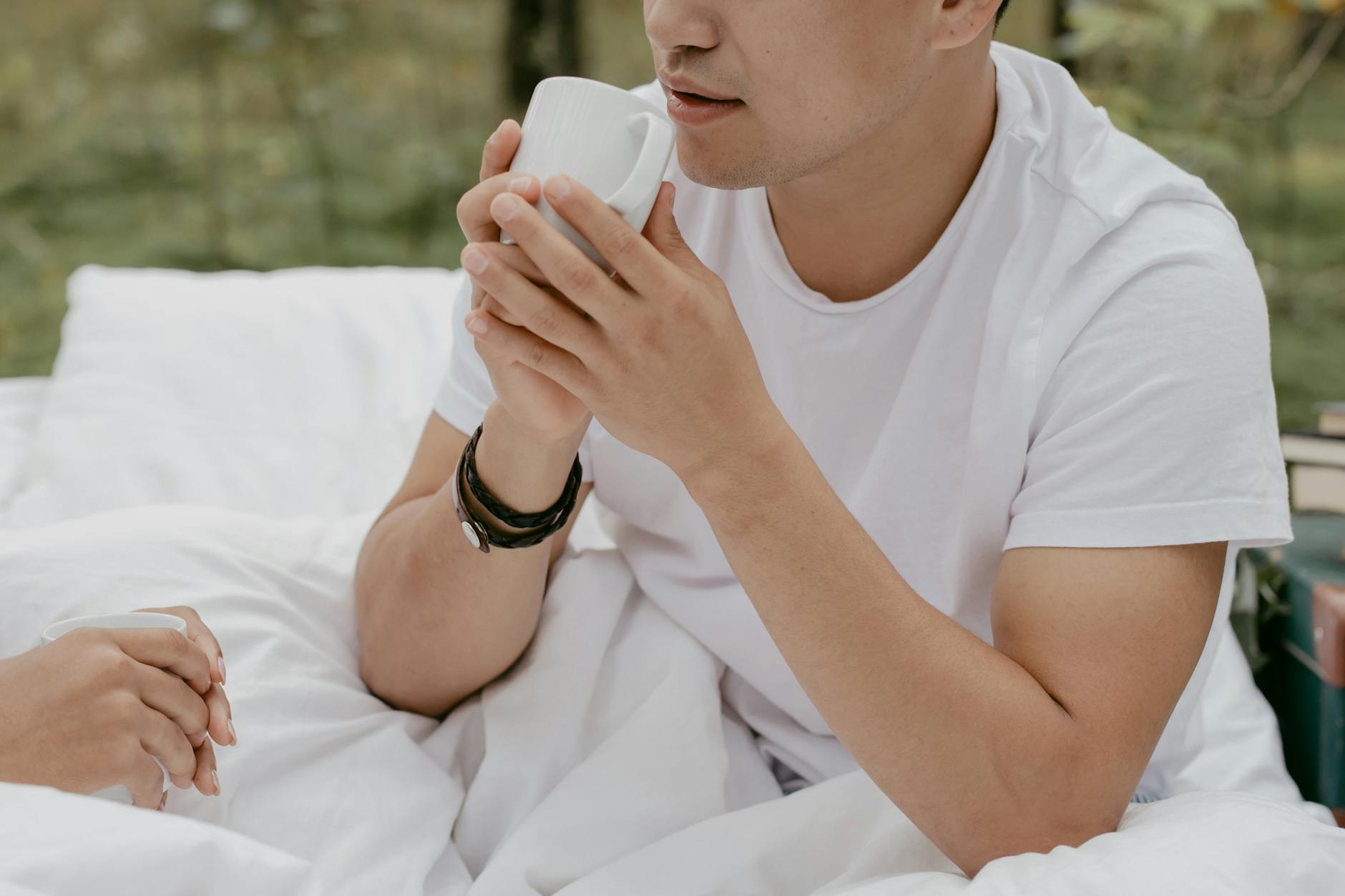

Overconsumption can cause your respiratory rate to increase even when you are sitting still. This happens because caffeine mimics the physiological effects of stress and prepares the body for physical exertion that is not happening. You might feel short of breath or notice that your breathing is shallow and fast. calming the nervous system by reducing caffeine allows your respiratory patterns to return to a relaxed state.
Excessive Sweating
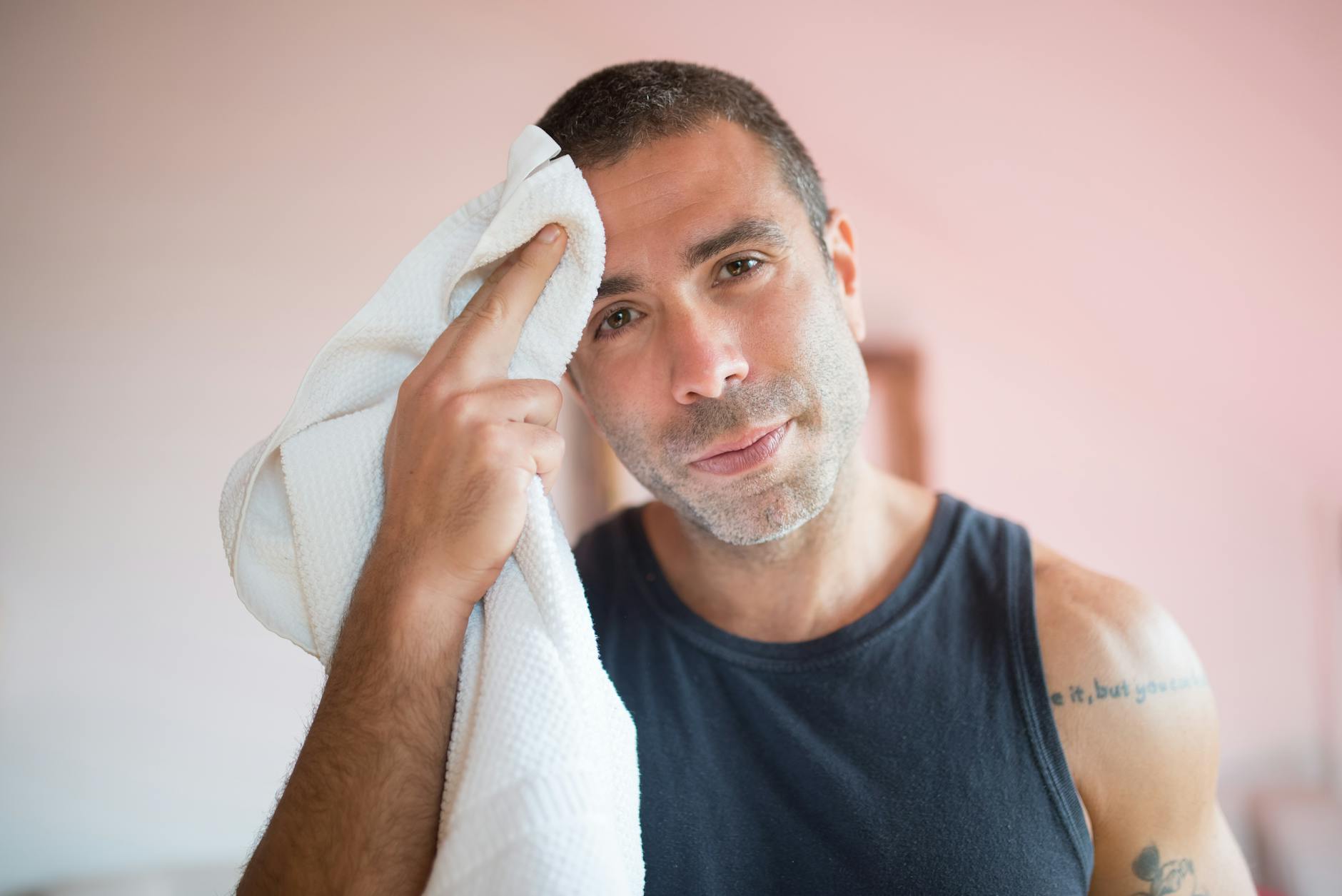

You might find yourself perspiring heavily even in cool temperatures or when you are not exercising. Caffeine activates the central nervous system and sweat glands which leads to increased perspiration. This creates a physical sensation of being overheated or flushed that can be socially uncomfortable. Hydrating with water instead of another cup of coffee helps regulate your body temperature.
Confusion or Brain Fog

While many drink coffee for focus taking too much can actually scatter your thoughts and make concentration difficult. The overstimulation disrupts cognitive processing and makes it hard to follow a single train of thought. You might find yourself jumping from task to task without completing anything effectively. Restoring clarity requires waiting for the caffeine to leave your system and getting adequate rest.
Nausea

Feeling sick to your stomach is a common physical reaction to toxic levels of caffeine. This often happens when coffee is consumed on an empty stomach or in rapid succession. The high acidity irritates the stomach lining and triggers a queasy sensation that makes eating difficult. neutralizing the acid with food and stopping intake usually settles the stomach.
Increased Thirst

Since caffeine pulls fluids from the body through urination you may experience a persistent feeling of thirst. Your mouth might feel dry or sticky as your body signals that it is becoming dehydrated. Ignoring this signal and reaching for more coffee only worsens the dehydration cycle. Drinking a glass of water for every cup of coffee is a good rule for maintenance.
Chest Pain

Experiencing tightness or pain in the chest area after drinking coffee is a serious symptom that requires attention. This occurs because the heart muscle requires more oxygen when it beats faster and harder due to stimulation. While it can mimic a heart attack it is often a sign of reduced blood flow to the heart. You should seek medical advice immediately if you experience chest pain associated with caffeine.
Restlessness

An inability to sit still or a constant need to move your legs is a telltale sign of caffeine overload. This psychomotor agitation makes relaxing or working at a desk feel physically uncomfortable. The body is primed for action due to the adrenaline spike and struggles to remain sedentary. Physical activity can help burn off the excess energy while you wait for the effects to subside.
Rambling Speech

Your speech patterns may become faster and less coherent as your brain races to keep up with the chemical stimulation. You might find yourself interrupting others or talking excessively without a clear point. This social symptom is often noticeable to those around you even if you do not perceive it yourself. Slowing down your intake helps restore a natural and conversational pace to your speech.
Facial Flushing

The sudden dilation of blood vessels near the surface of the skin can cause your face to turn red and feel warm. This reaction is similar to the flush caused by alcohol or intense exercise. It indicates that your circulatory system is reacting strongly to the stimulant in your bloodstream. The redness typically fades as the caffeine is processed and eliminated by the body.
Ringing in the Ears

Some individuals experience tinnitus or a ringing sound in their ears when their caffeine levels are too high. This auditory disturbance is linked to increased blood flow and blood pressure affecting the sensitive structures of the ear. It can be distracting and make it difficult to hear normal conversations or concentrate. eliminating caffeine usually stops the ringing and restores normal hearing function.
Dental Issues
High coffee intake exposes your teeth to significant amounts of acid and tannins which erode enamel and cause staining. You might notice increased sensitivity to hot or cold foods as the protective layer of your teeth wears down. Additionally many people grind their teeth when over-caffeinated which leads to jaw pain and wear. rinsing with water after coffee helps neutralize the acid and protect your smile.
Reduced Coordination

Excessive shaking and mental distraction can lead to clumsiness and a lack of fine motor control. You might find yourself dropping items or bumping into things more frequently than usual. This loss of physical precision occurs because the nervous system is firing signals too rapidly for smooth movement. lowering your dosage allows your brain and body to communicate more effectively.
Dependence

Feeling unable to function or start your day without coffee is a primary sign of physical addiction. You likely experience intense cravings and a sense that your brain is foggy until you have had your fix. This reliance means your body has altered its chemistry to accommodate the constant presence of the stimulant. weaning off slowly can help break the cycle of dependency without severe withdrawal.
Morning Grogginess
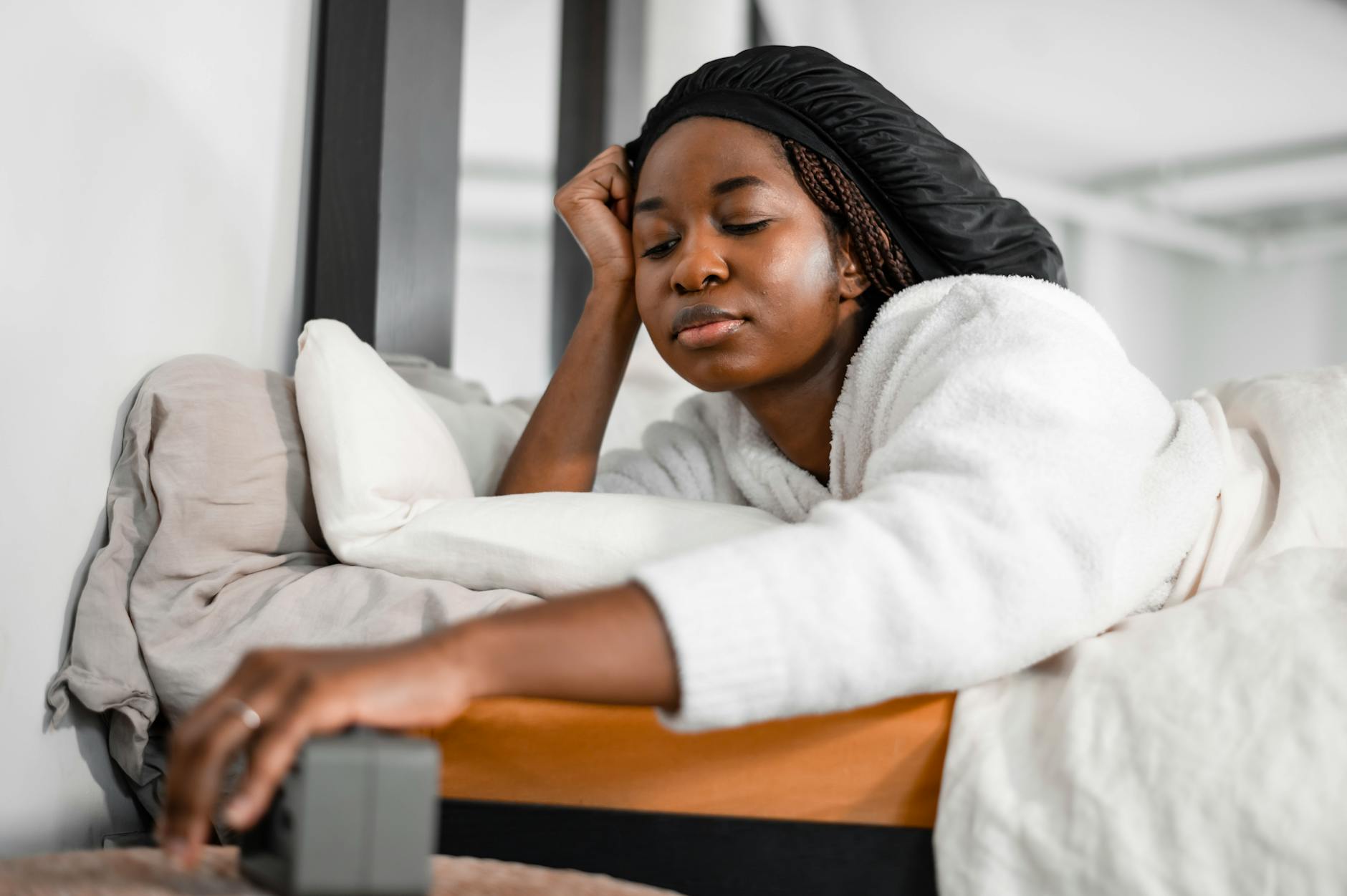

If you wake up feeling incredibly groggy and unrefreshed it may be due to caffeine withdrawal during the night. Your body processes the caffeine while you sleep and wakes up in a deficit state craving the substance to feel normal. This indicates that your baseline energy levels have been compromised by your habit. resetting your tolerance often leads to naturally higher energy levels in the morning.
Hallucinations

In very rare and extreme cases high doses of caffeine can lead to auditory or visual hallucinations. The intense stress placed on the brain causes it to perceive things that are not actually present. This is a severe sign of toxicity and indicates that the nervous system is overwhelmed. Immediate cessation of caffeine is necessary if reality testing becomes impaired.
Cold Sweats
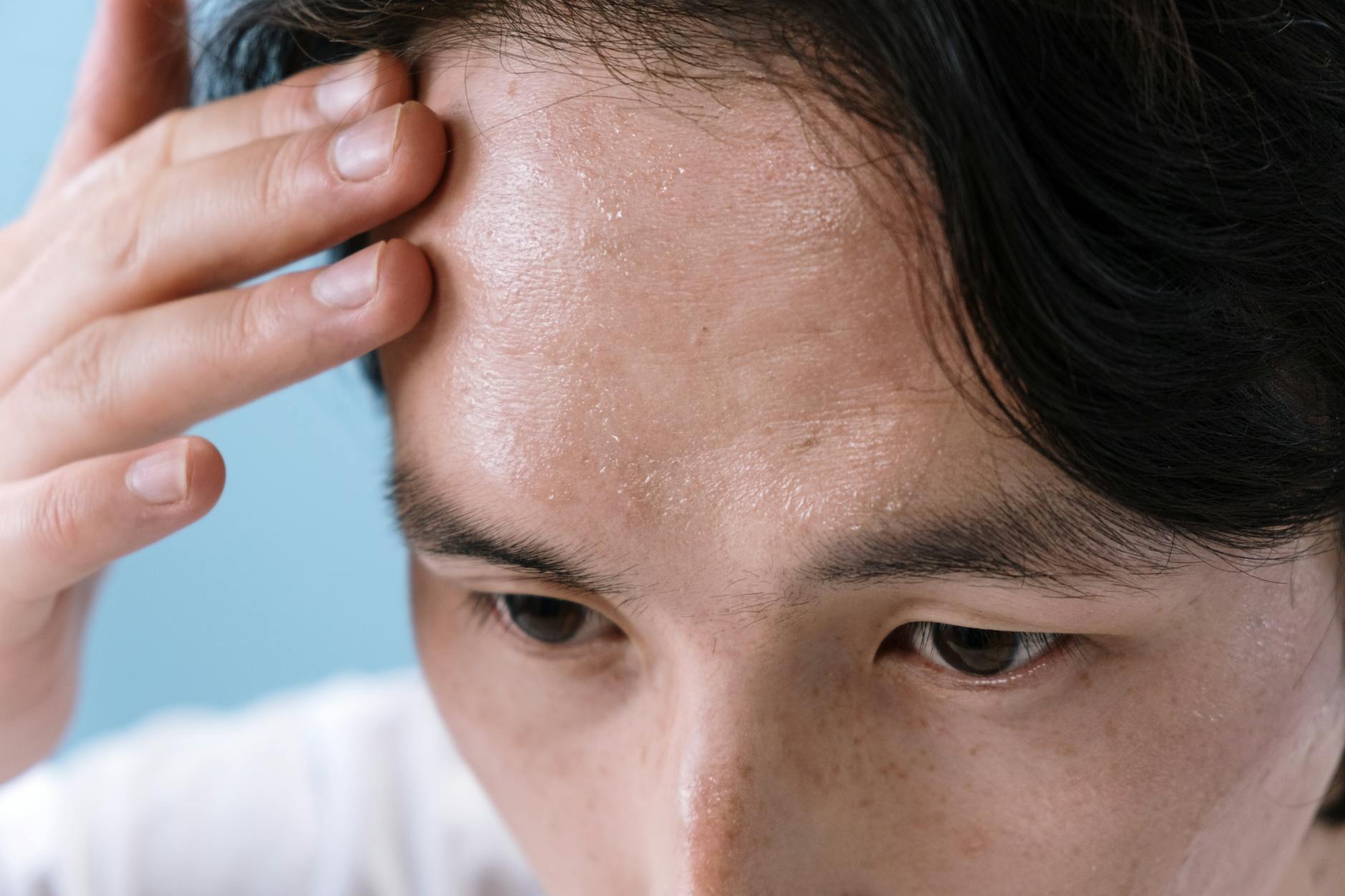

A sudden onset of clammy skin and cold sweat can occur as blood sugar levels fluctuate in response to caffeine. The stimulant affects insulin sensitivity and can cause rapid drops in glucose availability. This physical reaction leaves you feeling weak and shaky until you stabilize your blood sugar. Eating a balanced meal helps counteract these metabolic swings.
Emotional Instability

Wild mood swings from euphoria to depression can happen as the caffeine peaks and then crashes in your system. The manipulation of dopamine levels creates an artificial high that is unsustainable and leads to emotional volatility. You may feel great one moment and inexplicably sad or angry the next. stabilizing your caffeine intake helps maintain a consistent and positive emotional state.
We invite you to share your own experiences with caffeine and how you manage your intake in the comments.





